Robotic Prostatectomy: Comprehensive Insights and Analysis


Intro
Robotic prostatectomy is becoming a pivotal procedure in the management of prostate cancer. Surgeons use this advanced technique to enhance precision, reduce recovery time, and improve patient outcomes. Prostate cancer is prevalent among men, and effective treatments are essential for managing this life-altering condition. The evolution of surgical techniques has led to the integration of robotic systems, which include various sophisticated instruments designed to assist surgeons during the operation.
The goal of this article is to provide a nuanced understanding of robotic prostatectomy. By examining the mechanics, advantages, potential complications, and patient outcomes, we aim to forge a clear narrative that caters to both scholars and general readers alike. The importance of knowing the intricacies of this procedure cannot be overstated, as it represents a significant stride in minimally invasive surgery.
Background and Context
Overview of the Research Topic
Robotic prostatectomy stands at the intersection of technology and medicine. It offers minimally invasive options for patients diagnosed with prostate cancer, focusing on precision and safety. This section will elaborate on how such technology integrates into surgical practice. Robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, have transformed traditional methods, offering surgeons an advanced range of motion and enhanced visualization. This operation involves several key components, including surgical instruments controlled by the surgeon through robotic arms.
Historical Significance
The historical background of robotic prostatectomy extends back to the early 2000s. Initial trials focused on its feasibility compared to open surgery. The pivotal moment came when evidence suggested superior precision, reduced blood loss, and shorter recovery times. As advancements continued, robotic prostatectomy gained acceptance in many medical institutions globally. Studies showed that this technique, in many cases, resulted in better functional outcomes and lower complication rates compared to traditional approaches.
Robotic prostatectomy is not only a significant advancement in surgical technique, but it also paved the way for technological innovations in urology. Comprehensive training programs now emphasize robotic surgery, preparing the next generation of surgeons to master these systems.
Key Findings and Discussion
Major Results of the Study
Research indicates that robotic prostatectomy presents various benefits that are crucial for patient care. Some key findings include:
- Reduced Blood Loss: Patients experience less severe bleeding, which is often a risk in traditional prostate surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Many patients are discharged sooner than those who undergo open surgery.
- Lower Rates of Complications: Data shows fewer post-operative complications, such as infections and incontinence.
Detailed Analysis of Findings
The data collected from multiple studies indicates that robotic prostatectomy enhances surgical precision. Surgeons navigate through the robotic interface, allowing for better maneuverability in a confined space. This precision translates into lower impact on surrounding tissues, which can significantly affect recovery times and quality of life post-surgery. A meta-analysis of patients who underwent robotic prostatectomy suggests improved long-term outcomes, particularly concerning cancer control and functional recovery.
In light of these findings, it becomes apparent that the adoption of robotic systems in prostate cancer surgeries not only improves the sphere of surgical oncology but also encourages ongoing research into other minimally invasive techniques.
Intro to Robotic Prostatectomy
Robotic prostatectomy is a revolutionary development in the field of urological surgery. This surgical approach employs advanced robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing prostate gland removal with heightened precision and control. As the prevalence of prostate cancer continues to increase, understanding robotic prostatectomy becomes essential for patients, medical professionals, and researchers alike. The benefits of this technique include reduced recovery times, fewer complications, and improved postoperative outcomes for patients. However, this surgery also presents specific considerations that must be addressed.
Definition and Overview
Robotic prostatectomy refers to a surgical technique that utilizes robotic systems for the removal of the prostate gland. This method allows surgeons to operate with an enhanced view and greater maneuverability than traditional open surgery. The surgery primarily aims to treat prostate cancer but may also be indicated for benign prostatic hyperplasia in certain cases. Using instruments controlled by a surgeon allowing for small incisions, robotic prostatectomy provides more targeted approaches than conventional methods.
Historical Context
The evolution of robotic prostatectomy can be traced back to the introduction of robotic surgery in the late 20th century. Originally, robotic systems were used for various types of surgery, with the da Vinci Surgical System gaining prominence for urological procedures around the early 2000s. This innovation marked a significant shift in how prostate surgery was perceived, moving away from larger incisions and lengthy recovery periods. Over time, large clinical trials established the safety and efficacy of robotic prostatectomy, making it a preferred option among surgeons and patients.
Advancements in Surgical Technology
Robotic surgery has gone through remarkable advancements in technology. Modern robotic systems, such as the da Vinci platform, feature enhanced 3D visualizations, high-definition cameras, and articulated instruments that mimic human hand movements. The improvements in optics and instrument design lead to minimal blood loss and decreased surgical trauma. Also, innovations like enhanced anatomical mapping and real-time imaging during surgery are essential for achieving optimal outcomes. These technological developments continue to refine robotic prostatectomy, making it a benchmark for surgical excellence in the treatment of prostate conditions.
Robotic Surgery Mechanics
Robotic surgery mechanics play a crucial role in the efficacy and precision of robotic prostatectomy. The integration of specialized robotic systems allows for enhanced dexterity and visualization during surgical procedures. Understanding how these robotic systems operate provides vital insights for both practitioners and patients alike. It is important to note the various components that form these systems, their functionalities, and the collaborative dynamics among the surgical team. Each aspect contributes significantly to the outcome of the surgery and overall patient satisfaction.
Components of Robotic Systems
Robotic systems in prostatectomy typically consist of several interrelated components that work together to facilitate the surgery. The key components include:
- Robotic Console: This is where the surgeon sits and controls the robotic surgical instruments. It offers a three-dimensional view of the surgical field and allows for precise manipulation of tools.
- Patient-Side Cart: This includes robotic arms that hold and move the instruments. Each arm can operate independently, providing a level of flexibility that exceeds traditional surgery.
- Endoscopic Cameras: High-definition cameras provide clear images of the surgical field, allowing for enhanced visualization and detail during the procedure.
- Surgical Instruments: These are specifically designed tools that can be manipulated at various angles. They may include scissors, graspers, and other specialized tools.
With these components, the robotic system achieves a higher degree of accuracy and less invasiveness when compared to traditional open surgery.
Functionality of Robotic Instruments
The functionality of robotic instruments is central to the advantages offered by robotic prostatectomy. These instruments allow for precise movements that are often impossible with the human hand alone.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Robotic instruments are designed to be inserted through small incisions, minimizing tissue damage and reducing recovery time.
- Enhanced Range of Motion: The instruments can rotate and maneuver in ways that facilitate better dissection and suturing of tissues. This leads to improved outcomes, especially in delicate areas around the prostate.
- Tremor Reduction: The robotic system translates hand movements into smaller, more precise actions. This effectively reduces any tremor a surgeon might inadvertently introduce.
Such functionalities lead to improved surgical precision, which is often linked to reduced complications and faster patient recovery.
Role of the Surgical Team
The success of robotic prostatectomy relies heavily on the collaborative efforts of a skilled surgical team. Each member plays a pivotal role in ensuring the procedure's success.
- Surgeon: The primary operator controls the robotic system from the console. Their training and experience affect the procedure's outcomes significantly.
- First Assistant: Usually positioned at the patient-side cart, the first assistant helps with setup and may also assist during the surgery by manipulating instruments or cameras.
- Anesthesiology Team: They manage the patient's anesthesia and vital signs throughout the surgery, ensuring safety and comfort.
- Nursing Staff: They provide support by preparing the surgical instruments and ensuring that the operating room is equipped with everything needed for the procedure.


The dynamic between each member of the surgical team is vital. Effective communication and coordination can enhance the overall performance of the robotic surgery, ultimately influencing patient outcomes.
Effective teamwork in robotic surgery not only promotes a smooth operation but also minimizes risks associated with the procedure.
Surgical Indications
Criteria for Selection
The criteria for selecting patients for robotic prostatectomy are essential for ensuring the best possible outcomes. These criteria involve considering the stage of prostate cancer, the patient’s overall health, and any comorbid conditions. Early-stage prostate cancer is often a primary candidate for this surgical technique. The method is ideally suited for localized tumors, where cancer has not spread beyond the prostate gland.
Patients with significant pre-existing medical conditions may not be suitable candidates. The advantage of robotic surgery is its minimally invasive nature, which can mean less surgical trauma. However, extensive comorbidities can complicate anesthesia and recovery, impacting the patient’s candidacy.
Other important factors include age and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Younger patients tend to recover better and can have improved long-term outcomes. Elevated PSA levels may indicate more aggressive cancers, leading to different treatment paths.
Patient Psychological Considerations
Understanding patient psychology is a key part of the pre-operative assessment. Anxiety and fear can significantly affect a patient’s willingness to undergo surgery. The decision to pursue a robotic prostatectomy often arises from complex emotional and psychological factors.
Patients must be educated regarding the procedure and its implications. Knowledge about the benefits and risks can alleviate some anxiety. Some patients might struggle with the idea of robotic surgery, feeling uncertain about machine-assisted procedures.
Involving psychological support or counseling can be beneficial. Additionally, involving family members in the discussions may also help to ease patient concerns.
Patients who approach the surgery with a positive mindset generally experience better outcomes.
Staging and Grading Impact
Staging and grading are critical in determining the appropriateness of robotic prostatectomy. The staging of cancer assesses the tumor size and spread, while grading evaluates how aggressive the cancer cells appear under a microscope.
Localized tumors, which often fall into stage I or II, may yield better outcomes via robotic surgery. Higher-grade tumors may necessitate more comprehensive treatment plans, potentially overriding robotic options.
Moreover, thorough staging can influence post-surgical management decisions. If cancerous cells are noted to have aggressive characteristics, follow-up treatments may become necessary. This interplay between staging and grading further emphasizes the need for a well-founded decision-making process before proceeding to surgery.
"The effectiveness of robotic prostatectomy significantly hinges on accurate staging and grading, which guide both the surgical and post-surgical strategy."
Understanding these elements helps clinicians and patients alike anticipate and manage the trajectory of care better.
Procedure Overview
The procedure of robotic prostatectomy stands as a pivotal part of managing prostate cancer. Understanding this process is essential for both patients and medical professionals. It not only involves the intricacies of various surgical techniques, but also the preparation before surgery and the care following it. The goal is to ensure minimal complications and maximize recovery outcomes.
The procedure encompasses several stages. Each stage is crucial, from the pre-operative preparation to the actual surgical intervention, and finally the post-operative care. This thorough overview helps demystify the surgical experience for patients while informing physicians about the systematized approach needed for optimal care.
Pre-operative Preparation
The journey towards robotic prostatectomy begins long before the patient enters the operating room. Pre-operative preparation involves a series of evaluations to assess not only the patient’s physical health but also psychological readiness. It begins with thorough diagnostics, including imaging studies and laboratory tests. A complete understanding of the patient’s medical history is crucial, guiding the surgical team in their planning.
Patients may undergo:
- Blood work
- Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans
- Risk assessments for anesthesia
Understanding the patient's emotional state is equally necessary. Discussions about the surgery, its implications, and expected outcomes can alleviate anxiety, fostering a cooperative atmosphere.
Intra-operative Techniques
As patients transition into the operating environment, skilled surgeons utilize advanced robotic systems to conduct the procedure. The key here lies in the execution of intra-operative techniques. The surgeon’s expertise combined with the precision of robotic instruments allows for enhanced visibility and control.
When performing the prostatectomy, the use of robotic arms with specialized instruments represents a major advancement. The critical techniques used include:
- Laparoscopic vision: This provides high-definition visualization of the surgical area.
- Bilateral nerve-sparing techniques: These minimal interference methods aim to preserve nerve function, thereby minimizing post-surgical side effects.
- Tissue resection: The use of robotic tools enables precise excision of cancerous tissues with reduced blood loss.
Post-operative Protocols
After the robotic prostatectomy is completed, attention turns towards recovery. Post-operative protocols play a vital role in ensuring patient safety and promoting healing. Patients are typically monitored in recovery rooms before being moved to standard inpatient wards or discharged home.
A few significant post-operative protocols include:
- Pain management: Effective analgesia is essential for comfort.
- Monitoring for complications: Vigilance for signs of bleeding or infection is critical.
- Rehabilitation planning: Early mobilization contributes to faster recovery and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Motivating follow-up appointments are also important. They allow medical personnel to assess recovery, manage any complications, and reinforce the importance of ongoing care.
"Post-operative care represents the bridge between surgical intervention and full recovery, ensuring optimal patient outcomes."
Overall, the procedure overview encompasses an array of important elements. By highlighting each of these, it becomes clear that successful outcomes from robotic prostatectomy rely heavily on meticulous preparation, skilled execution, and extensive post-operative care.
Comparative Efficacy
Evaluating the comparative efficacy of robotic prostatectomy entails understanding its advantages and disadvantages relative to traditional surgical methods. The preference for one surgical technique over another often hinges on certain performance metrics and patient outcomes. Insight into these comparisons assists surgeons, patients, and researchers in making informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Robotic vs. Traditional Open Surgery
Robotic prostatectomy introduces a minimally invasive approach compared to the traditional open surgery. The critical distinction lies in the level of precision and the technique used to remove cancerous tissues. Robotic systems, like the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to operate with enhanced visualization and greater dexterity. This contrasts with open surgery, which utilizes larger incisions and often results in more trauma to the body.
- Benefits of Robotic Surgery:
- Limitations of Robotic Surgery:
- Reduced bleeding and postoperative pain.
- Shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times.
- Lower incidence of complications such as infections.
- High costs associated with the robotic equipment and its maintenance.
- Extended learning curve for surgeons to gain proficiency.
Research shows that robotic prostatectomy may result in comparable cancer control rates when set alongside traditional approaches. Studies indicate that patients often report better functional outcomes, including the preservation of erectile function and urinary continence, making it a favorable option for many.
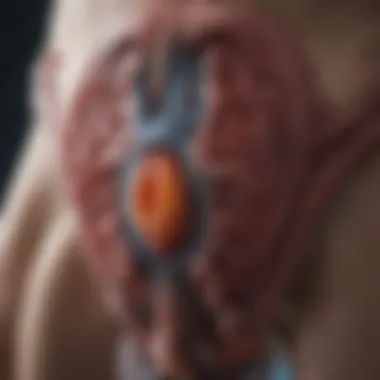

Methodological Considerations in Studies
Understanding the reliability of studies evaluating robotic prostatectomy is essential for valid conclusions. The methodology adopted can influence the interpretation of results significantly. Several factors must be recognized:
- Study Design: Randomized controlled trials offer stronger evidence than observational studies.
- Sample Size: Larger samples can provide more accurate estimates of the effectiveness and safety of the intervention.
- Follow-Up Duration: Longer follow-ups facilitate the understanding of long-term outcomes, such as recurrence rates and quality of life.
These methodological considerations help clarify if the findings are generalizable to the broader population. Careful examination of data encourages evidence-informed approaches to patient treatment plans.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
Patient-reported outcomes are pivotal in evaluating the success of robotic prostatectomy. These outcomes encompass patients' perceptions related to their health status and quality of life post-surgery.
- Common Concerns:
- Urinary incontinence and sexual function are crucial areas evaluated.
- Patients often highlight the importance of prompt return to normal activities.
Surveys and questionnaires deployed within research often reflect satisfaction levels and ongoing issues post-operatively. The feedback enables practitioners to refine surgical techniques and improve pre- and post-operative counseling for patients.
In summary, understanding comparative efficacy not only supports informed decision-making but also enhances patient care in robotic prostatectomy. The ongoing advancement in surgical technologies will further influence these comparisons.
Risks and Complications
The discussion of risks and complications is crucial in understanding robotic prostatectomy. Even though robotic surgery offers clear advantages, such as precision and reduced recovery time, it is not without its issues. Patients and clinicians must be aware of potential risks associated with surgery to make informed decisions. A deep dive into surgical risks, long-term complications, and risk assessment protocols can provide valuable insights into the overall framework of robotic surgery and prostate cancer treatment.
Potential Surgical Risks
Robotic prostatectomy is a minimally invasive procedure, yet it carries inherent surgical risks. These include bleeding, infection, and injury to surrounding organs. Such injuries may lead to complications like bladder or rectal perforation or damage to nerves affecting erectile function. While the precision of robotic systems reduces the likelihood of such incidents compared to traditional open surgery, it does not eliminate them entirely.
The significance of these risks cannot be understated. Choosing a well-trained surgical team can help mitigate them. Awareness of potential complications prior to surgery is essential for patients, as it can influence their decision-making process.
Long-term Complications
Long-term complications are another vital consideration for patients undergoing robotic prostatectomy. Common complications include urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Approximately 10% to 30% of patients may experience varying degrees of these issues after surgery, depending on factors such as age and pre-operative condition.
Research indicates that many patients experience improvement in these conditions over time, but some may have persistent challenges. Understanding these potential long-term effects is crucial for patients to manage expectations post-surgery. Additionally, discussing these outcomes with the medical team can inspire greater confidence in addressing future health concerns.
Risk Assessment Protocols
To effectively navigate the complexities of surgical risks and complications, implementing robust risk assessment protocols is essential. These protocols involve thorough pre-operative evaluations, which include laboratory tests, imaging studies, and assessments of patients' overall health. By examining individual risk factors like age, comorbidities, and cancer stage, clinicians can tailor surgical approaches that minimize complications.
In some cases, advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans can provide improved visualization of tumor margins and surrounding tissues. Incorporating this information into pre-operative planning is vital for improving surgical outcomes and minimizing risks.
"Comprehensive pre-operative evaluation is an essential part of surgical planning that can significantly reduce complications and improve patient outcomes."
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery and rehabilitation are critical phases following robotic prostatectomy. Understanding these aspects contributes significantly to the overall success of the surgical procedure. Patients generally require a structured plan for recovery that addresses both physical healing and psychological well-being, as both can impact quality of life.
Post-operative Care Requirements
After undergoing robotic prostatectomy, patients must adhere to specific post-operative care requirements designed to minimize complications and promote healing. This usually involves the following elements:
- Rest and Activity Management: Patients are advised to rest adequately after the procedure. Gradually increasing activity levels is essential, but patients should avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercises during the early weeks of recovery.
- Wound Care: Proper care of the surgical site is important to prevent infections. Patients will receive instructions on how to clean the area and what signs of infection to look for.
- Medication Management: Prescribed medications may include pain relievers and antibiotics. Adhering to the medication schedule is vital for comfort and infection prevention.
- Fluid Intake and Diet: Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet are crucial. Patients are often recommended to start with clear liquids before gradually introducing solid foods.
Following these guidelines can make a significant positive difference in recovery time and outcomes.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Monitoring and follow-up appointments are vital components of recovery. These sessions provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess recovery and address any concerns that may arise. Key considerations include:
- Regular Follow-ups: Patients typically have follow-up appointments within a few weeks post-surgery. These visits may involve blood tests, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, to monitor for cancer recurrence.
- Symptom Tracking: Patients are encouraged to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider. Symptoms can include pain, difficulty urinating, or unexpected changes in health.
- Rehabilitation Sessions: Some patients may benefit from structured rehabilitation programs focused on restoring physical fitness, especially if they experience complications or limitations post-surgery.
Effective monitoring ensures that potential issues can be identified and managed early.
Patient Quality of Life Considerations
Quality of life is an essential aspect of recovery after robotic prostatectomy. The surgical procedure can affect several areas of a patient's life, and it is crucial to address these considerations:
- Physical Well-being: Many patients experience changes in urinary function and sexual health following surgery. Counseling and support groups can be helpful for coping with these changes and improving physical comfort.
- Psychological Impact: The emotional response to cancer treatment can vary. Patients may feel anxiety, depression, or concerns regarding their health. Access to mental health professionals may assist patients in managing emotional well-being.
- Support Systems: Engaging family and friends in the recovery process can provide significant emotional support. Patients are encouraged to lean on their networks to ease the transition back to daily activities.
"The key to a successful recovery lies not only in the surgical outcome but also in addressing the multi-dimensional aspects of a patient’s life."
Overall, recovery and rehabilitation are essential for maximizing the benefits of robotic prostatectomy. A well-rounded approach focusing on physical, emotional, and social reintegration offers the best chance for a positive outcome.

Future of Robotic Prostatectomy
The future of robotic prostatectomy is pivotal in shaping the landscape of surgical interventions for prostate cancer. This section aims to elucidate how advancements in technology, surgical training, and ongoing research are expected to transform patient care. The focus lies on the integration of emerging tools, the development of enhanced training protocols, and the exploration of innovative research directions that may enhance surgical precision, patient safety, and overall outcomes.
Emerging Technologies in Robotics
Emerging technologies are at the forefront of redefining robotic prostatectomy methodologies. Developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to play a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of robotic systems. These technologies can analyze procedural data in real-time, potentially assisting surgeons in making more informed decisions. Moreover, advancements in imaging techniques, such as augmented reality and high-definition 3D visualization, promise to improve the surgeon’s ability to navigate complex anatomical structures with greater accuracy.
Furthermore, miniaturization of robotic instruments contributes to less invasive approaches, which can lead to reduced recovery time for patients. Innovations such as flexible robotic arms and enhanced haptic feedback systems allow for greater dexterity in the operating room. This evolution not only improves the technical aspects but also significantly impacts patient outcomes, making robotic prostatectomy a more favorable option.
Advancements in Surgical Training
The effectiveness of robotic prostatectomy heavily relies on the skills and training of the surgical team. As the field evolves, surgical education must also adapt to new technologies. Comprehensive training programs incorporating simulation-based learning and virtual reality are gaining traction. These immersive learning environments provide resident surgeons and operating teams with opportunities to practice procedures without risk to patients.
In addition, mentorship programs led by experienced robotic surgeons allow for knowledge transfer that is essential in mastering the nuanced skills of robotic surgery. Emphasizing hands-on experience complements theoretical knowledge, ensuring that new surgeons are well-prepared to handle complex situations during actual procedures. This increased emphasis on advanced training methodologies is likely to yield proficient surgeons capable of optimizing patient care and outcomes.
Research Directions and Innovations
Ongoing research is crucial to the progress of robotic prostatectomy. Investigations are increasingly focused on refining surgical techniques, understanding long-term patient outcomes, and enhancing technological interfaces. Collaboration between medical professionals and engineering teams fosters innovation that addresses current gaps in robotic surgical capabilities. Notable research directions include studies on optimizing surgical pathways to minimize complications and exploring the long-term effects of robotic surgery on patient quality of life.
Moreover, there is a growing interest in patient-tailored approaches, where individual patient anatomy and pathology are taken into account when planning robotic procedures. This could entail the development of personalized robotic systems capable of adapting to specific surgical needs. The integration of patient data analytics and robotic technology may also lead to predictive modeling of surgical outcomes.
"The future is not just about the technology itself, but how we utilize it to enhance patient care."
In summary, the future of robotic prostatectomy involves a continuous interplay between emerging technologies, surgical proficiency, and innovative research efforts. As these elements converge, the landscape of prostate cancer treatment will likely transform, leading to higher standards of surgical care and improved patient outcomes.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the realm of robotic prostatectomy as the integration of advanced technology into surgical practice raises various moral questions. This section elucidates the importance of addressing these ethical dilemmas, particularly as they pertain to informed consent, access to surgical resources, and the broader implications on healthcare economics. Understanding these elements is fundamental for medical professionals, patients, and the society at large, as choices made in the operating room resonate beyond the sterile environment, influencing public health policy and individual patient outcomes.
Informed Consent Challenges
Informed consent is a foundational principle in medical ethics, ensuring that patients are fully aware of the risks and benefits of a procedure. In the context of robotic prostatectomy, informed consent challenges may arise due to the complexity of the technology involved. Patients may not fully understand the distinctions between robotic-assisted surgery and traditional methods. Clear communication is vital; surgeons must explain the specific nature of robotic prostatectomy, including its technological mechanics, expected outcomes, and potential complications.
- Complexity of Information: The technical jargon used in robotic surgery can create barriers. Medical professionals must tailor their communication to match the patient’s level of understanding.
- Time Constraints: Surgeons often face time limits during consultations which can hinder comprehensive explanations, potentially leading to ill-informed decisions.
- Emotional Factors: Patients are often anxious when facing prostate surgery, which can impair their ability to absorb information fully.
Overall, effective informed consent in robotic prostatectomy requires continuous effort and adaptation to ensure clarity.
Access and Resource Allocation
Access to robotic prostatectomy is another ethical concern, particularly regarding disparities in healthcare. High costs and limited availability of robotic surgical systems can create barriers for all patients, especially those in lower-income brackets. The allocation of resources must be scrutinized to ensure equitable access to high-quality surgical care.
- Geographic Disparities: In some regions, advanced robotic systems may only be available in urban medical centers, limiting rural patients' access.
- Insurance Limitations: Not all insurance providers cover robotic prostatectomy comprehensively, making it unaffordable for some patients.
- Availability of Trained Professionals: There might be a lack of adequately trained robotic surgeons in certain areas, exacerbating the access problem.
Ensuring equitable access to robotic prostatectomy is paramount in fostering a just healthcare system.
Impact on Healthcare Economics
The incorporation of robotic prostatectomy into clinical practice has significant implications for healthcare economics. The technology can be expensive, necessitating considerable investment in both machinery and training. However, these costs need to be weighed against the potential benefits of enhanced patient recovery and reduced hospitalization times.
- Cost vs. Outcome: While robotic procedures tend to come with higher initial costs, they may lead to shorter recovery periods, possibly decreasing overall treatment expenses.
- Market Dynamics: The development of robotic surgery has propelled a market for surgical robots, creating competition that can lead to price reductions.
- Long-term Healthcare Savings: Improved surgical outcomes could lead to fewer long-term complications and reduced need for additional treatments, ultimately contributing to cost savings for the healthcare system.
Analyzing these economic factors reveals the necessity of integrating ethical considerations with financial realities.
Investing in robotic prostatectomy technology is not merely a medical decision; it is an ethical one that affects patient lives, equitable access, and healthcare economics.
Finale
The conclusion of the article serves to encapsulate the key elements discussed throughout the sections, emphasizing the significance of robotic prostatectomy within modern surgical practices. This section synthesizes findings, highlighting how robotic-assisted procedures can enhance surgical outcomes and patient experiences.
Summary of Findings
Robotic prostatectomy demonstrates notable advancements in treating prostate cancer, offering several advantages over traditional surgical methods. Key findings include:
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients often experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activities.
- Minimized Complications: Compared with open surgery, robotic procedures may result in fewer post-operative complications.
- Improved Precision: Robotic instruments allow for greater precision and control, enhancing the surgeon's ability to navigate complex anatomical structures.
These factors contribute to overall improved patient satisfaction and outcomes, affirming the role of robotic surgery in contemporary urological practices.
Recommendations for Future Research
Future research should focus on several pivotal areas to further the understanding and application of robotic prostatectomy:
- Longitudinal Studies: Investigating long-term outcomes for patients undergoing robotic prostatectomies compared to other methods.
- Technological Innovations: Exploring emerging technologies that may enhance the precision and efficiency of robotic systems.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: A thorough examination of the economic implications of utilizing robotic surgery, factoring in both direct costs and broader healthcare resources.
- Psychosocial Impact: Evaluating the psychological and emotional effects on patients before and after robotic surgery could provide valuable insights for holistic treatment approaches.
Final Thoughts on Robotic Surgery
The evolution of robotic surgery, particularly in prostatectomy, underscores a paradigm shift in surgical treatment approaches. As technology continues to advance, it holds the potential to revolutionize the way urological procedures are performed. Embracing robotic techniques may lead to improved surgical outcomes, but it is equally essential to address the challenges that accompany this innovation, such as training healthcare professionals and ensuring equitable access.
In summary, robotic prostatectomy represents a significant leap forward in urological surgery. Its advantages are well-documented, and ongoing research will be critical in refining techniques, expanding usage, and optimizing patient outcomes.







