Mastocytoma in Adults: Insights on Management

Intro
Mastocytoma, while often associated with children, poses significant challenges in adults as well. This condition, characterized by an abnormal proliferation of mast cells, can manifest in various forms, leading to a spectrum of symptoms that can be both puzzling and debilitating. Unlike its pediatric form, adult mastocytoma tends to present with different clinical features and may require distinct management strategies. Understanding the implications of this condition in adults is critical, as it informs both diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Background and Context
Overview of the Research Topic
Mastocytoma is a relatively rare neoplasm of mast cells, which are a type of immune cell involved in allergic responses and inflammation. These cells contain granules rich in histamine and other mediators, which can lead to a host of symptoms when released into the body. In adults, mastocytoma can occur as either solitary mastocytoma or systemic mastocytosis, each presenting different challenges in terms of management and implications for long-term health. This distinction is crucial, as it guides healthcare providers in formulating appropriate treatment plans.
Historical Significance
The study of mastocytoma dates back to the early 20th century, when researchers first began to identify and categorize various forms of mast cell disorders. While early descriptions were often limited by the technological constraints of the time, progress in histopathology and immunology has illuminated many aspects of these conditions. In particular, adult mastocytoma remains under-researched compared to its pediatric counterpart. This gap highlights the need for a modern perspective on adult presentations, reflecting how diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes have evolved.
Key Findings and Discussion
Major Results of the Study
Recent studies have revealed critical insights into the etiology and clinical presentation of adult mastocytoma. For instance:
- Incidence Rates: Adult mastocytoma is rarer than in children, complicating diagnosis due to the low familiarity among clinicians.
- Symptom Variability: Symptoms can range from localized skin lesions to systemic reactions, significantly affecting quality of life.
- Diagnostic Challenges: The manifestations often overlap with other conditions, necessitating a diligent diagnostic process that may include skin biopsies, serum tryptase levels, and allergen testing.
Detailed Analysis of Findings
Understanding the findings from recent research sheds light on effective management strategies.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: It is essential to involve specialists such as dermatologists, allergists, and oncologists in the management plan, ensuring that all aspects of the patient’s health are considered.
- Tailored Therapies: Treatment options may include antihistamines, corticosteroids, and in some instances, newer therapies like tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which target specific cellular pathways. Each case should be evaluated individually to ascertain the best course of action.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Managing adult mastocytoma is not just about treating symptoms but also understanding the long-term risk of progression to more severe forms, such as systemic mastocytosis. Close monitoring and regular follow-up care are critical components of effective management.
"Addressing the individual needs of adult patients with mastocytoma requires a comprehensive understanding of the disease's nuances, emphasizing why a one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective."
Prolusion to Mastocytoma in Adults
Mastocytoma remains a seldom-discussed condition, yet understanding it is pivotal for effective management among adults. Unlike pediatric mastocytoma, adult cases often present unique challenges that require specialized knowledge and attention. The implications of this rarity can be profound, contributing not only to diagnostic dilemmas but also to the psychosocial aspects faced by those diagnosed.
Delving into this subject helps unravel the complexities surrounding mastocytoma, equipping healthcare professionals with the tools necessary for accurate identification and appropriate treatment. Adults diagnosed may experience a myriad of symptoms; therefore, acknowledging mastocytoma's implications can lead to better quality of care.
Definition of Mastocytoma
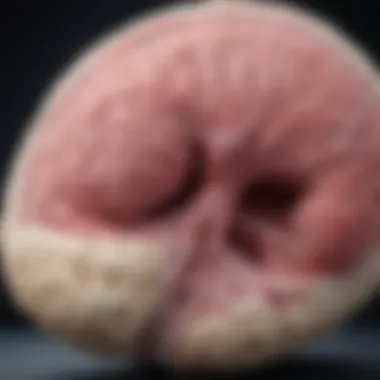
Mastocytoma refers to a localized proliferation of mast cells, a type of immune system cell that plays a vital role in allergic responses and inflammation. In adults, it is predominantly represented as a cutaneous entity. The lesions are often dark brown or reddish in appearance and can vary from a small bump to larger, more extensive skin involvement. This condition isn't merely a cosmetic concern; it often intertwines with broader systemic implications, affecting the patient's health dynamics.
Historical Context
The history of mastocytoma is steeped in evolving medical understanding. Initially, the awareness and documentation of mast cell-related disorders were sparse, but as dermatological studies advanced, so did the recognition of mastocytoma's significance in adult populations. In the earlier part of the 20th century, researchers grappled with basic classifications of skin lesions, and mastocytoma was often eclipsed by other more prominent dermatological conditions.
"While advances in medicine have illuminated many aspects of skin pathology, mastocytoma remains somewhat of an unsung hero in dermatological discourse."
By the latter half of the century, however, the integration of immunohistochemistry and better diagnostic tools led to a clearer understanding of mastocytoma's histological features, differentiating it from other similar presentations. This trajectory emphasizes how crucial ongoing education and research are in shaping our comprehension of mastocytoma and, consequently, provides a more sophisticated foundation for future therapeutic approaches.
In summary, as we explore this condition in adults, not only do we highlight its definition and historical context, but we also set the stage for a deeper understanding of its pathophysiology and clinical implications.
Epidemiology of Mastocytoma in Adults
Understanding the epidemiology of mastocytoma in adults lays a crucial foundation for grasping its clinical significance, coverage for future research, and the overall healthcare management strategies for the condition. This section shines a light on how prevalent this specific neoplasm is among adults and examines the various demographic factors that influence its occurrence. Knowledge about the epidemiology can guide clinicians in recognizing symptoms and formulating effective treatment plans. It also plays a vital role in raising awareness about the disease among the populace, which can lead to early detection and intervention.
Prevalence and Incidence
Mastocytoma is not exactly a common sight in a typical clinical setting. It’s relatively rare, with estimates suggesting an incidence of about 1 to 2 cases per 100,000 adults annually. However, this can vary by region and population. The prevalence tends to be underreported, as many cases may go undiagnosed or misclassified due to the often subtle symptoms resembling allergic reactions or other skin disorders.
Several studies show that males are slightly more affected than females, but this difference isn't particularly striking. The disease is most commonly detected in adults aged 30 to 50, an important detail that practitioners might take into consideration when evaluating patients presenting with skin lesions or other related complaints. The slow progression and often localized nature of mastocytoma can lead to a delay in diagnosis, which contributes to the lack of accurate incidence figures.
Demographic Variations
Demographics also play a role in the understanding of mastocytoma. For instance, regions with higher sun exposure might report different outcomes, as UV exposure may influence mast cell behavior. Race and ethnicity can also influence presentation; some studies hint that certain racial backgrounds may predispose individuals to a higher risk.
- White individuals generally show a higher prevalence compared to those of African descent or Asian populations.
- Interestingly, geographical variations do exist in reporting cases, possibly due to environmental factors or genetics.
Factors such as socioeconomic status can influence access to healthcare, leading to variations in diagnosis rates. Adults from higher socioeconomic backgrounds are often more aware of health issues, leading to earlier detection compared to those from lower socioeconomic groups.
Understanding these demographic variations is essential, not only for effective healthcare planning but also for tailoring patient education and awareness campaigns, ensuring that high-risk groups receive adequate attention and resources.
"Prevalence data can be informative, but they don’t paint the full picture. We must consider access, awareness, and even local healthcare practices."
Overall, a comprehensive grasp of the epidemiology of adult mastocytoma helps in spotlighting the importance of continued research and the need for appropriate healthcare policies that can cater to those affected by this uncommon yet impactful condition.
Pathophysiology of Mastocytoma
Understanding the pathophysiology of mastocytoma is crucial to grasp the complexities of this rare neoplasm of mast cells in adults. This section dives into the underlying mechanisms that give rise to the condition, shedding light on how these mast cells go awry and manifest clinically. By exploring mast cell biology and pivotal genetic factors, one can appreciate the multifaceted nature of mastocytoma and the implications for diagnosis and treatment.
Mast Cell Biology
Mast cells are integral components of the immune system, primarily involved in inflammatory responses and allergic reactions. They originate from hematopoietic stem cells and are found in tissues throughout the body, particularly in the skin, lungs, and digestive tract. In a healthy state, mast cells patrol the body for pathogens, releasing mediators like histamine, cytokines, and growth factors as needed. However, in mastocytoma, these cells undergo abnormal proliferation or accumulation.
The pivotal element to grasp here is that mastocytoma results from dysregulation of mast cell growth pathways, often tied to mutations in key genes. A significant mutation observed in adult mastocytoma is in the KIT gene, responsible for producing a protein that influences mast cell growth and function. When these genes are mutated, they lead to excessive mast cell proliferation, accumulation, or inappropriate activation, which in turn triggers the condition's characteristic symptoms and complications.
As mast cells multiply unchecked, they can infiltrate skin and internal organs, causing a range of symptoms from skin lesions to systemic reactions. Understanding this biology helps inform clinicians on potential avenues for treatment and management strategies that could address these root causes, not just the symptoms.
Genetic Factors
The genetic factors associated with mastocytoma provide significant insights into its pathophysiology. Different mutations may contribute to the disease's development, with the KIT mutation being the most widely studied. This mutation is found in a considerable percentage of patients, providing clues about the etiology of mastocytoma. When alterations occur in the cellular signaling pathways related to the KIT gene, you may see a transformational shift in mast cell behavior, leading to malignancy.
Apart from the KIT gene, other genetic anomalies have been noted that could influence the disorder's course. These may include variations in genes that regulate cell survival, apoptosis, and immune responses. As such, the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers remains an area of active research. Researchers are exploring how factors such as chronic infections, allergens, or even environmental toxins may interact with these genetic susceptibilities.
"Understanding the genetic implications of mastocytoma is like solving a complex puzzle; every piece reveals more about the condition's behavior and management."
Furthermore, comprehending these genetic factors is important for developing targeted therapies. With advancements in genetic profiling, it is becoming feasible to tailor treatments based on specific genetic alterations in individual patients, thereby improving therapeutic outcomes.
In summary, exploring the pathophysiology of mastocytoma through mast cell biology and genetic factors enhances clinicians' understanding and informs their approach to diagnosis and treatment. This knowledge not only aids in recognizing the disorder earlier but also paves the way for developing innovative therapeutic strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Clinical Manifestations
Understanding the clinical manifestations of mastocytoma is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. These manifestations serve as the foundational indicators upon which further investigatory measures can be executed. As a condition that frequently presents with a diverse array of symptoms, mastocytoma’s implication extends beyond mere physical signs; it influences the patient's quality of life and overall health. Recognizing symptoms early can improve prognostic outcomes and tailor treatments to individual needs, ensuring a personalized approach to what can be a puzzling condition.
Cutaneous Symptoms
Cutaneous symptoms are often the first points of concern for patients with mastocytoma. These symptoms manifest primarily on the skin, which can be both distressing and visually striking for patients. Notably, the most characteristic cutaneous presentation includes raised lesions, known as urticaria pigmentosa, which are often brownish to tan in color and can vary in size.
- Lesions: These may sometimes itch or urticate with pressure, heat, or trauma—this phenomenon is known as Darier’s sign.
- Flushing: Flushing or localized redness might also frequently accompany these lesions.
- Skin Pruritus: Patients often report intense itching, exacerbating emotional distress and sometimes leading to secondary skin infections from scratching.
Overall, these cutaneous manifestations can significantly affect a patient’s social interactions and mental health, illustrating that management must incorporate both dermatological and psychological support.
Systemic Symptoms
Mastocytoma isn't just a skin-deep condition; systemic symptoms can present themselves, complicating the clinical picture further. Some common systemic manifestations include:


- Hypotensive Episodes: Patients may experience sudden drops in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or fainting.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain can arise due to mast cell degranulation, which releases various mediators affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Fatigue: Many individuals report general fatigue and malaise, often dismissing these as commonplace symptoms in a busy lifestyle.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Asthma-like symptoms or difficulty breathing may occur in reaction to environmental triggers due to mast cell activity.
Addressing these systemic manifestations is vital, as they may require multi-faceted treatment strategies, potentially making use of pharmacological interventions to stabilize mast cell behavior.
Variability in Presentation
One of the striking aspects of mastocytoma in adults is the variability in symptom presentation. Not every patient exhibits the same signs or severity; differences can stem from numerous factors including:
- Individual Health Factors: Age, concurrent health conditions, and genetic predispositions can all influence how mastocytoma presents.
- Lesion Location: The site of mastocytomas, whether they are cutaneous or systemic, can dictate the symptom burden on patients.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain environmental agents may escalate mast cell reactions in some individuals, adding another layer of complexity to symptom presentation.
This variability means that no two cases of mastocytoma are alike. As such, healthcare professionals need to approach each case uniquely, tailoring assessment and intervention strategies to the patient’s individual experience.
Understanding the clinical manifestations of mastocytoma allows clinicians to pinpoint diagnoses more effectively, leading to improved treatment pathways and quality of life.
Engaging with these manifestations in detail is essential for researchers and practitioners alike who aim to deepen their understanding of this complex and often misunderstood condition.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing mastocytoma in adults is a complex affair, necessitating a methodical approach to ensure accurate identification and effective management. The diagnostic components built around clinical evaluation, imaging techniques, and biopsy and histopathology form a cornerstone for understanding the disease. Each layer of this diagnostic framework is aimed at revealing the multifaceted nature of mastocytoma, enabling healthcare professionals to devise tailored strategies for intervention.
Clinical Evaluation
Clinical evaluation stands as the initial gateway in diagnosing mastocytoma. It involves a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history, combined with an examination of symptoms, which often vary greatly in affected individuals. Mastocytoma can manifest in several forms—cutaneous, systemic, or both—which makes the clinician's assessment essential.
During this phase, the healthcare provider looks for characteristic signs such as urticaria pigmentosa and various other skin lesions. The presence of diffuse or localized mast cell infiltrates is crucial. Moreover, understanding the patient's previous allergic reactions or anaphylactic episodes contributes immensely to the overall clinical picture.
A comprehensive evaluation might include:
- A detailed past medical history of related conditions.
- A focused physical examination, looking for skin changes or systemic signs.
- A review of family health history, especially any patterns of mast cell disorders.
Gathering these details allows for an informed and directed approach to further investigation. Ultimately, the clinical evaluation lays down a solid baseline, guiding subsequent diagnostic tests.
Imaging Techniques
Once a clinical suspicion is solidified, imaging tends to follow. This segment of the diagnosis is particularly integral for understanding the extent and location of mastocytoma. Imaging techniques can include ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They serve the crucial role of identifying any internal masses and assessing overall organ involvement.
For instance:
- Abdominal ultrasound can reveal whether there are hepatic or splenic involvements, often a consideration in systemic mastocytosis.
- CT scans offer cross-sectional views and provide essential information regarding potential lymph node enlargement and distant organ involvement.
- MRI is sometimes preferred for soft tissue characterization and gives detailed images, critical for discerning the nature of lesions.
However, caution is essential, as not all mastocytomas are visible through imaging, especially if they are small or if they exist primarily in the skin without internal manifestations. Each imaging modality brings its strengths and limitations, thus necessitating judicious selection based on individual patient cases.
Biopsy and Histopathology
Finally, biopsy and histopathology form the final, definitive diagnostic modality for mastocytoma. A tissue biopsy remains the gold standard in establishing the diagnosis, as it offers a conclusive view of mast cell proliferation under microscopic examination.
The biopsy can be accomplished both through excisional procedures or fine needle aspiration, depending on the location and type of mastocytoma present. Once obtained, histological analysis can reveal crucial details such as:
- The presence of clonal mast cells, indicated by specific staining methods that target mast cell mediators.
- The degree of mast cell infiltration and whether the pattern aligns with mastocytoma characteristics.
In the absence of histologic confirmation, the likelihood of misdiagnosis increases, highlighting the critical role of this step.
Conclusively, integrating these diagnostic approaches—clinical evaluation, imaging, and histopathological examination—provides a comprehensive strategy that addresses the complexity of mastocytoma in adults. Each component interlocks to form a sophisticated diagnostic framework that not only ensures accurate identification but also informs subsequent management plans.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis plays a crucial role in the management of mastocytoma in adults. This process involves distinguishing mastocytoma from other medical conditions that may present with similar symptoms. Given that mastocytoma often manifests with cutaneous lesions, such as hives or flushes, it is essential for healthcare professionals to carefully consider a range of potential diagnoses. Accurate differentiation not only impacts patient outcomes but also can significantly affect treatment choices.
Conditions Simulating Mastocytoma
Several conditions may mimic the manifestations of mastocytoma, leading to misdiagnosis if not properly identified. Some of the notable ones include:
- Urticaria: Characterized by welts and itching, it can easily be confused with mastocytoma. Understanding the triggers and duration of the symptoms can help differentiate between the two.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: This common skin cancer might display irregular patches that superficially resemble the lesions of mastocytoma. A thorough examination and possibly a biopsy are needed to distinguish between these two diagnoses.
- Dermatographism: This condition causes raised welts on the skin from light scratching, which can simulate the whealing associated with mastocytoma. Observing the pattern and timing of the skin response is critical in accurately assessing the condition.
- Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria: Similar in nature to mastocytoma, this long-lasting form of hives can lead to confusion during evaluation.
Understanding these conditions is vital not only for diagnosis but for directing the appropriate management plans. By recognizing the differences, clinicians are better equipped to implement suitable treatments.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective management of mastocytoma. Here's why it matters:
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Each condition requires a unique approach. Misdiagnosing could mean administering treatments that are ineffective or even harmful.
- Avoiding Complications: Some conditions, if left untreated or treated improperly, can result in significant complications. For instance, mistaking mastocytoma for a simple allergy can delay necessary care.
- Improved Prognosis: The earlier and more accurately a mastocytoma is diagnosed, the better the likelihood of successful long-term management. Studies have indicated that timely intervention can lead to better quality of life for patients.
- Resource Allocation: Accurate diagnosis helps in allocating medical resources efficiently, ensuring that patients receive the right care at the right time. This is especially crucial for rarer conditions where specialized care may be necessary.
"In the realm of mastocytoma, clarity in diagnosis is not simply beneficial; it is paramount for successful therapeutic outcomes."
Longevity and quality of life are significantly related to proper diagnosis and subsequent treatment avenues. As such, both medical professionals and patients must understand the importance of accurate differential diagnosis in managing this complex condition.
Therapeutic Strategies
The management of mastocytoma in adults requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual patient. Each patient’s response to treatment can vary significantly, making it crucial to explore various therapeutic strategies. The aim is not just to alleviate symptoms but also to address the root causes effectively.
Surgical Management
Surgical intervention often stands at the forefront when addressing mastocytoma. The primary objective is to excise the tumor completely, minimizing the risk of recurrence. This method is especially beneficial for localized mastocytomas.
Key Considerations:
- Extent of Disease: Prior to surgery, imaging studies are essential to assess the size and locations of the mastocytoma.
- Margins: Achieving clear margins can significantly reduce recurrence rates. It is important for the surgeon to plan the incision carefully.
- Postoperative Care: After surgery, patients may need careful follow-ups to monitor their recovery and any possible complications.
Overall, surgical management provides a clear methodology to tackle mastocytoma head-on, making it a crucial part of treatment.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological options play a pivotal role in managing symptoms associated with mastocytoma, especially when surgery isn't sufficient or feasible. These treatments aim primarily at controlling symptoms such as itching, flushing, and anaphylactic reactions.
Common Medications Include:
- Antihistamines: Such as cetirizine or loratadine, help alleviate urticaria and itching.
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation, especially in cases with systemic involvement.
- Mast Cell Stabilizers: Like cromolyn sodium, may also be prescribed to prevent mast cell degranulation.
These medications not only improve the quality of life but also help curb the severity of reactions related to mastocytoma.
Immunotherapy Options
Immunotherapy is emerging as a potential avenue for treatment, particularly in cases that are refractory to conventional therapies. While research is ongoing, its significance grows as we understand more about the immune system’s role in mast cell disorders.
Potential Approaches:
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Some studies explore the effectiveness of agents targeting mast cells directly.
- Including Checkpoint Inhibitors: These may enhance the immune response against the mast cells associated with mastocytoma.
As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms behind mastocytoma, immunotherapy might offer promising outcomes, paving the way for future strategies.
In summary, therapeutic strategies covering surgical management, pharmacological treatments, and immunotherapy options play critical roles in tackling mastocytoma in adults. Combining these approaches is likely to yield the best results, tailoring the course of treatment to the specific needs of each patient.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes


Understanding the prognosis and long-term outcomes of mastocytoma in adults is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. This knowledge not only helps in preparing for potential complications but also enables informed decision-making regarding treatment options. Prognosis refers to the expected course of the condition and its potential outcome, while long-term outcomes focus on the quality of life and survivability of patients after diagnosis and treatment.
Survival Rates and Recurrence
When we talk about survival rates for adult mastocytoma, it's essential to acknowledge the rarity of the condition. Different studies suggest various survival rates, typically contingent upon factors like age, overall health, and treatment modalities. As for recurrence, studies have shown that mastocytomas can sometimes reoccur even after seemingly successful treatment. Therefore, patients are often advised to have regular follow-ups for monitoring, ensuring any resurgence is caught early on.
The effectiveness of treatment also affects survival statistics. Surgical intervention tends to yield better outcomes for localized mastocytomas. However, complications may arise in cases with systemic involvement or metastatic disease. Patients might find themselves navigating a murky landscape, with treatment success varying significantly.
"Prognosis in mastocytoma can be a moving target; each individual's story adds a unique thread to the fabric of understanding this condition."
Signs of recurrence can include new skin lesions, systemic symptoms, or unexpected fluctuations in well-being, underscoring the importance of consistent monitoring, even after treatment. Therefore, establishing a safety net through regular check-ups not only helps in enhancing survival rates but also provides reassurance to patients and their families.
Quality of Life Considerations
The implications of mastocytoma extend beyond mere survival; quality of life plays an equally critical role. Patients often grapple with the daily ramifications of their condition, which may include skin irritations, sensitivity to environmental factors, or fatigue caused by systemic symptoms. These difficulties can severely impact their overall well-being.
Quality of life considerations hinge on several factors:
- Physical health: The presence of symptoms like itching and painful skin lesions can disrupt day-to-day activities, placing additional emotional strain on individuals.
- Mental health: Anxiety can stem from unpredictability in symptoms and the fear of recurrence.
- Social interactions: Patients might experience social withdrawal, whether due to stigma or simply the discomfort of symptoms.
Considering these factors, a mixed approach to treatment is often advisable. Integrating psychological support with medical treatments could lead to more favorable outcomes in quality of life. Support groups, counseling, and community resources often play a crucial part in helping patients feel less isolated, offering them a network of understanding peers who can share their journeys.
Overall, recognizing the critical sway that prognosis and long-term outcomes have on daily living allows for a more comprehensive approach to patient care, stressing the importance of holistic management in overcoming the challenges presented by adult mastocytoma.
Mastocytoma and Comorbidities
The intersection of mastocytoma and comorbidities is a pivotal topic because it sheds light on how the presence of other conditions can influence the outcome and management of mastocytoma. Understanding these connections is critical for both practitioners and patients, providing insight into a comprehensive approach to care. Mastocytoma, a condition that often presents with a host of symptoms, can create complex scenarios when paired with other health issues. This dual burden may affect treatment options, disease progression, and the patient's overall quality of life.
Impact on Other Conditions
Mastocytoma can significantly affect coexisting health conditions. For instance, individuals suffering from allergic disorders may find that their symptoms are exacerbated due to the mast cell activation characteristic of mastocytoma. This activation can increase histamine release, leading to heightened allergic reactions or intolerance to medications that would typically be well-tolerated by individuals without mastocytoma. Patients with gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome might also experience more severe symptoms as mast cells play a role in gut permeability and inflammation.
Moreover, there's the concern of how mastocytoma interacts with chronic illnesses like asthma or cardiovascular diseases. Chronic illnesses often require complex medication regimes, and a patient burdened with mastocytoma might find themselves in a situation where drug interactions could pose significant risks. Its important to stay on top of the levels of medicine they are taking and always consult healthcare professionals before making changes.
By recognizing these impacts, medical teams can better calibrate patient treatments keeping in mind the various health spectrums affecting each individual.
Management of Coexisting Disorders
Effective management of coexisting disorders in patients with mastocytoma requires a multidisciplinary approach. This means healthcare providers must communicate and collaborate closely, sharing insights and strategies for effective treatment.
- Care Plans: Creating a comprehensive care plan that accommodates both mastocytoma and any comorbid conditions is vital. Each health issue should be logged, and the management of one should account for the others.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups and check-ins are necessary to gauge how treatments for one condition may affect another. This ongoing evaluation can help minimize risks and adjust therapies as needed.
- Patient Education: Equipping patients with information is paramount. Patients should understand how mastocytoma might influence their existing conditions and vice versa. Knowledge empowers them to take part in their treatment and communicate effectively with their healthcare providers.
- Holistic Approaches: In some cases, integrating complementary therapies alongside conventional medicine may prove beneficial. Nutritional support, physical therapy, and stress management techniques can offer additional relief for many patients.
In summary, understanding the relationship between mastocytoma and comorbidities is crucial for optimizing patient care. Fostering communication between specialists and creating tailored treatment plans is fundamental to navigating the complexities faced by these patients.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Teams
Effective management of mastocytoma in adults hinges on the collaborative efforts of a multidisciplinary team. This team typically consists of various specialists, including dermatologists, oncologists, immunologists, and patient educators. Each professional contributes unique expertise that enhances patient care and ensures a holistic approach for managing this condition. The essence of this collaboration is to combine knowledge across fields, leading to more accurate diagnosis, tailored treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
Benefits of Multidisciplinary Approaches
Having a variety of specialists involved means that patients receive well-rounded care. For instance, a dermatologist may focus on cutaneous symptoms while an oncologist assesses the potential for systemic involvement. This teamwork allows for:
- Personalized Treatment: Each team member can provide insights that contribute to a customized approach, adjusting therapies based on individual patient reactions.
- Comprehensive Care Plans: By pooling knowledge, the team can create detailed care strategies that address all aspects of mastocytoma.
- Continuity of Care: Regular communication within the team facilitates monitoring of treatment effectiveness and timely adjustments as needed.
"In the realm of complex conditions like mastocytoma, no specialist operates in a vacuum; collective insights pave the way for breakthroughs that benefit the patient."
Collaboration for Optimal Care
Collaboration is key to optimal care in mastocytoma management. Each specialist brings something different to the table. For example, while a hematologist monitors blood parameters and systemic health, an allergist might evaluate and manage potential allergic reactions linked to mast cell activation. Such teamwork requires structured communication, regular meetings, and established protocols to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Key elements for effective collaboration include:
- Regular Interdisciplinary Meetings: Scheduled discussions allow team members to share observations and develop coordinated treatment plans.
- Shared Patient Records: Integrated electronic health records (EHR) systems can help avoid misunderstandings and lapses in care.
- Patient-Centric Focus: The ultimate aim is to make patients active participants in their treatment, reinforcing that they are at the heart of the collaboration.
Case Management Strategies
Implementing effective case management strategies is crucial in the multidisciplinary approach to mastocytoma. This involves not only clinical evaluations but also addressing psychological and social aspects of the patients' journey. For instance, navigating the mental health landscape is just as important; many patients experience anxiety or depression stemming from their diagnosis.
Considerations for successful case management include:
- Establishing a Case Manager Role: A dedicated professional who coordinates between different specialists and the patient can streamline the process.
- Follow-Up Protocols: Regular check-ins with the patient increase adherence to treatment and allow for timely interventions if complications arise.
- Resource Accessibility: Providing patients with educational resources about mastocytoma, workshops on coping strategies, and peer support groups can be equally important.
Patient Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about mastocytoma is crucial, given its rarity and the complexity surrounding its diagnosis and treatment in adults. How patients understand their condition significantly affects their journey towards management and support. Awareness encompasses recognizing symptoms, understanding treatment options, and acknowledging the importance of regular follow-ups. The benefits of an informed patient base cannot be overstated; it leads to earlier diagnosis, better management strategies, and a reduced sense of isolation.
Understanding the Condition
To tackle mastocytoma effectively, patients must grasp what this condition entails. Mastocytoma is a neoplasm primarily involving mast cells, which have an integral role in immune response. However, when these cells proliferate abnormally, it can lead to both skin-related symptoms and systemic issues. Patients ought to familiarize themselves with various manifestations of mastocytoma, which include the presence of brownish or reddish skin lesions, intense itching, and in some cases, systemic symptoms such as gastrointestinal discomfort or cardiovascular issues. Understanding the biological behavior of mast cells aids individuals in recognizing when things might not be right, prompting timely medical attention.
Awareness also extends to the genetic factors related to mastocytoma. While most cases arise sporadically, a subset is linked to inherited genetic mutations. Patients should be mindful of their family health histories, as this can guide discussions with healthcare providers about genetic counseling or testing.
Empowering Patients through Information
In the realm of mastocytoma, information is empowering. When patients arm themselves with knowledge, they can engage in meaningful conversations with their healthcare teams. This not only fosters a better relationship with providers but ensures that patient's concerns and preferences are part of the treatment planning process.
Regular access to updated information about mastocytoma treatments encourages patients to consider a variety of options, from surgical procedures to novel pharmacological therapies. Knowing the potential side effects and benefits allows patients to weigh their choices more thoroughly.
Additionally, educational resources available online or through support groups can provide invaluable guidance. Here are some effective methods for patients to gather information:
- Reputable Websites: Websites like Wikipedia and Britannica provide foundational knowledge.
- Support Groups: Social media platforms like Reddit have forums where individuals discuss their experiences, sharing coping strategies and real-life insights.
- Healthcare Providers: Engaging in open discussions with dermatologists or oncologists specializing in mastocytoma ensures that patients receive tailored information relevant to their unique cases.
"Knowledge not only empowers patients, it also enhances the quality of life by reducing anxiety related to the unknown."
By ensuring that patients understand the nuances of their condition and feel equipped with accurate information, healthcare professionals can make significant strides toward better patient outcomes and satisfaction in managing mastocytoma.
Current Research Directions
The landscape of mastocytoma research is rapidly evolving, reflecting the ongoing pursuit of a deeper understanding of this complex condition. New findings and innovative approaches are critical to enhancing the current treatment protocols and improving patient outcomes. Researchers are concentrating on multiple facets, from understanding the genetic underpinnings of mast cell neoplasms to exploring novel therapeutic strategies. The exploration in this direction is not just beneficial for patients with mastocytoma, but also for the larger field of oncology.
Innovative Therapies Under Investigation
In recent years, the spotlight has turned toward several innovative therapies that hold promise for individuals diagnosed with mastocytoma. Some notable examples include:
- Targeted Therapy: Medications specifically designed to inhibit pathways involved in mast cell proliferation. These treatments aim to selectively target and eliminate cancerous cells while sparing healthy tissue, thereby reducing side effects.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: The use of antibodies that can specifically target and bind to mast cells may provide a mechanism to neutralize their activity. This approach is garnering attention for its potential efficacy in treating systemic symptoms.
- Small Molecules: Compounds that can disrupt the signaling pathways that contribute to mast cell activation or growth are under investigation. Their ability to work at the molecular level makes them appealing candidates for therapy.
- Gene Therapy: There is ongoing research that focuses on correcting the genetic abnormalities present in mast cells. Although still in the early stages, gene therapy offers the potential for a fundamental solution to mastocytoma.
Researchers also emphasize on the importance of clinical trials, which are essential for validating the efficacy of these new treatments. Thus, maintaining an open dialogue among clinicians, researchers, and patients not only helps in prioritizing the most pressing questions in mastocytoma research but also keeps the enthusiasm up for those looking for breakthroughs in treatment.
Evolving Understandings of Mastocytoma
The comprehension of mastocytoma has significantly expanded over the last few years, unveiling aspects that were previously not well understood. Some key developments in research include:
- Genomic Studies: Advances in genomic technologies have enabled researchers to examine the genetic makeup of mastocytomas, identifying specific mutations or alterations that are crucial in disease development. Such insights lead to more personalized treatment plans, tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Microenvironmental Factors: Understanding how the tumor microenvironment impacts mast cell behavior has become a focal point. It appears that neighboring cells and the surrounding stroma can influence the growth and behavior of mastocytomas, potentially offering new avenues for treatment.
- Immune Response Characteristics: The interaction between mast cells and the immune system is another evolving area. Research indicates that mast cells possess unique immune-modulatory properties that may play a role in not only the pathology of mastocytoma but also in how patients respond to therapy.
This continual evolution in the understanding of mastocytoma's biology underscores the necessity for an adaptive approach in both research and clinical management. By fostering collaboration and communication between scientists and practitioners, the potential for groundbreaking advancements in the field remains strong.


"Research is not just about finding answers but refining the questions we ask."
Overall, the current research directions in mastocytoma promise exciting advancements that could transform the clinical landscape of this rare neoplasm.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
Mastocytoma in adults brings along a plethora of hurdles when it comes to accurately diagnosing and effectively treating the condition. Recognizing these challenges is crucial for healthcare practitioners and patients alike. The struggles in pinpointing the right diagnosis can stem from the overlapping symptoms with other dermatological disorders, creating a perfect storm of confusion during evaluations. Moreover, treatment options can often fall short of expectations. Understanding these dynamics not only informs better clinical decision-making but also prepares patients for the ups and downs of managing their health.
Barriers to Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of mastocytoma stands as a significant hurdle in the management process. Firstly, one major barrier is the rarity of the condition itself. Since mastocytoma is less common in adults compared to children, many healthcare providers might not easily recognize the signs. The symptoms often manifest as skin lesions, which could easily be misdiagnosed as other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
Furthermore, the histological similarities between mastocytoma and other mast cell disorders can muddle the waters during biopsy evaluations. For instance, it’s not uncommon for a thorough examination to yield ambiguous results, leading to either delayed or incorrect diagnoses. The consequence of such a scenario could mean that patients miss out on timely intervention strategies that are tailored to their specific condition.
"The longer the delay in diagnosis, the more complicated the management becomes, as patients might endure unnecessary treatments that do not address the underlying issue."
Another significant factor contributing to diagnostic difficulties is the variability of presentations in mastocytoma. Some patients might present with mild symptoms that do not prompt immediate concern, causing delays in pursuing more definitive diagnostic measures. In addition, healthcare providers may lack the awareness or training to ask the right questions or perform the necessary tests to differentiate mastocytoma from more prevalent conditions.
Limitations of Current Treatments
The journey of treating mastocytoma often resembles walking through a maze: it can be complex and filled with uncertainties. Current treatments for mastocytoma, while effective to some degree, have notable limitations. Firstly, surgical excision, commonly employed as a treatment method, isn’t always feasible. Complete removal of lesions might not be possible in cases where the mastocytoma infiltrates surrounding tissues. This leaves a significant portion of patients facing the reality of a recurrent condition.
Pharmacological interventions also have their shortcomings. Although antihistamines can assist with symptom relief, they do not address the root cause of mastocytoma. Moreover, the response to medications can be unpredictable; what works wonders for one patient may not have the same effect on another. Some patients may find themselves in a relentless cycle of trying various drug therapies, searching for what might provide relief without any guaranteed success.
The use of immunotherapy is another avenue explored in recent years. While promising, this approach is still largely experimental for mastocytoma and isn't universally available. Consequently, many patients might be left with limited options for managing their condition effectively.
Impact of Mastocytoma on Daily Life
Mastocytoma, although often overlooked, carries significant implications for those diagnosed as adults. Understanding how this condition influences daily life is crucial. Patients face a myriad of challenges, from physical symptoms to emotional strife. The effects can ripple through various aspects of their existence, shaping not just their health but also their interpersonal relationships and professional commitments. This section explores both the tangible adjustments patients must make and the often neglected psychological impacts.
Daily Living Adjustments
Living with mastocytoma may necessitate a range of adjustments in day-to-day activities. Patients often find themselves having to tailor their routines to accommodate their condition.
- Dietary Changes: Many individuals notice that certain foods trigger symptoms. Consequently, they might steer clear of spicy dishes or alcohol. It’s not uncommon for patients to maintain a food diary to pinpoint what exacerbates their reactions.
- Lifestyle Alterations: Exercise routines may also have to change. While maintaining physical health is important, patients may need to avoid activities that cause overheating or excessive strain, which could provoke systemic symptoms.
- Environment Adaptations: Where a person lives can significantly affect their quality of life. For instance, those living in high-humidity areas might struggle more than others, leading them to consider relocating. Even minor environmental controls, like air conditioning or humidifiers, can make a world of difference.
- Medication Management: Many patients have to juggle a complex regimen of medications. Keeping track of prescriptions and dosing schedules can transform into a daily chore. Some might adopt digital programs to remind them about their medications and manage side effects.
These adjustments, while necessary, can feel burdensome, leading to a sense of frustration or helplessness. Yet, some patients find empowerment in making these choices, allowing them to take control of their health in a way that fits their lifestyle better.
Psychosocial Implications
The impact of mastocytoma goes beyond the physical. Psychosocial factors play a considerable role in the overall experience of the disease.
- Anxiety and Stress: The unpredictability of symptoms can contribute to heightened levels of anxiety. When will the next reaction occur? How severe will it be? These questions may lead individuals to feel a constant sense of vigilance that permeates their lives.
- Social Isolation: Some individuals may avoid social gatherings, fearing potential reactions or the scrutiny of others. This withdrawal can create feelings of loneliness and isolation. Friends and family might find it hard to understand the condition, leading to strained relationships.
- Self-Esteem Challenges: As appearances can be affected due to skin lesions or reactions, some can struggle with self-esteem. The visibility of the disorder does not go unnoticed; patients may feel they are always under the watchful gaze of society, breeding insecurity about their appearance.
- Support Systems: On a positive note, many patients find strength in support networks. Whether through online forums or local groups, connecting with others facing similar challenges provides a sense of community. Sharing experiences can foster resilience and better coping strategies.
Understanding the psychosocial implications of mastocytoma is as critical as recognizing its physical effects. It's a comprehensive part of care that needs consideration.
In summary, the consequences of mastocytoma in adults extend deeply into everyday life, impacting both practical routines and emotional well-being. Recognizing these factors plays a vital role in fostering a supportive atmosphere and devising effective management strategies.
Future Perspectives in Mastocytoma Management
The discussion surrounding mastocytoma is much more than just about understanding the disease's current state; it’s about peering into the horizon to see what advancements lie ahead. This part of the article highlights the prospects that may redefine how we approach the management of mastocytoma in adults. It’s essential to investigate emerging treatments and technologies to understand the potential shift in paradigms regarding patient care. The given research in this realm is vital, not just for healthcare professionals, but also for patients navigating this condition.
Emerging Treatments and Techniques
The landscape of treatment options for mastocytoma is evolving. New therapies are cropping up like spring flowers, each offering a glimmer of hope for patients who have struggled with this uncommon condition.
- Targeted Therapy: This approach focuses on specific molecular targets involved in the pathogenesis of mastocytoma. For instance, the use of Imatinib, an inhibitor that targets specific pathways in relevant cell growth, has shown promise in some cases.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Developing monoclonal antibodies that target mast cells could provide another avenue for treatment, potentially allowing for tailored therapeutic regimens based on the patient's specific condition and overall health.
- Gene Editing Technologies: CRISPR and other gene-editing tools have started making waves in the medical community. The potential to correct genetic predispositions to mast cell abnormalities opens doors not seen before. As research continues, some enthusiasts argue that this could one day become a standard treatment option rather than something relegated to experimental labs.
Notably, the commitment to clinical trials has been unwavering. Patients who participate in trials often gain access to cutting-edge treatments before they're widely available. Thus, keeping abreast of recent developments is crucial for best outcomes.
Potential for Improved Outcomes
As these innovative treatments emerge, the potential for improved outcomes cannot be overstated. The benefits extend far beyond a laboratory study. They directly affect patients' lives, with tangible improvements seen in areas such as:
- Symptom Management: Enhanced therapies aim to alleviate symptoms that disrupt daily life, making it easier for individuals to maintain a semblance of normalcy.
- Prognosis: With newer treatments on the market, there’s an optimistic view toward survival rates and minimizing recurrence. Advancements in personalized medicine create hope for developing a plan as unique as the patient themselves.
"In a quick-paced world, staying informed about mastocytoma's directional shifts is not merely beneficial; it's critical for effective management."
Not only does this shift aid clinical practice, but it also enhances the psychological and emotional well-being of those affected. Knowing that continuous improvements could herald a brighter future can be incredibly reassuring.
Facilitating discussions between professionals and patients regarding these advancements plays a vital role in fostering understanding and acceptance of ongoing treatment plans. As the health sector becomes more adept at utilizing these novel approaches, it will ultimately pave the way towards better management strategies, helping many find a path that was previously clouded in uncertainty.
Finale
Understanding the complexities surrounding mastocytoma in adults is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. This unique condition, while rare, poses significant implications for diagnosis, treatment, and overall management. Each facet of this discussion underscores the necessity of a tailored approach—one that considers the distinct etiology and clinical manifestations that adults experience.
Summary of Key Insights
Mastocytoma presents various challenges, and some of the key insights from this article include:
- Diverse Clinical Presentation: Adult mastocytoma does not manifest identically to its pediatric counterpart. Symptoms can vary significantly from one individual to another, necessitating a keen clinical eye for accurate diagnosis.
- Importance of Multidisciplinary Teams: Collaboration among specialists—from dermatologists to oncologists—ensures that all aspects of a patient’s condition are addressed. This not only aids in achieving better treatment outcomes but also enhances the quality of life for those affected.
- Innovative Research Directions: Ongoing studies are paving the way for novel therapies and treatment modalities, which hold the promise of better management strategies for adult mastocytoma patients.
Overall, the article aims to equip the reader with a thorough understanding of mastocytoma and emphasize the importance of broadening the knowledge base surrounding rare neoplasms.
Final Thoughts on Future Research
The landscape of mastocytoma research is ever-evolving. As more is learned about the genetic and biological underpinnings of this condition, it becomes clear that the path forward involves:
- Fostering Collaborative Research Initiatives: Engaging with various research institutions can lead to breakthroughs that single entities might not achieve alone.
- Encouraging Patient Participation in Studies: Patients should be included in research initiatives, giving them a voice and potentially leading to findings that are relevant to their lived experiences.
- Prioritizing Longitudinal Studies: Observing patients over extended periods will provide critical insights into long-term outcomes and the efficacy of treatment strategies.
Investing in future research is not merely about finding cures; it is about enhancing the quality of life for those impacted by mastocytoma. By continuing to push boundaries in understanding this rare neoplasm, we can hope to make meaningful strides in patient care and management.
References and Further Reading
The subject of mastocytoma, especially in adults, dives deep into complex medical intricacies that can leave even seasoned practitioners scratching their heads. This is where comprehensive references and further reading come into play. Having a well-rounded understanding of this condition relies heavily on accessing diverse resources that not only elucidate its pathophysiology but also explore current management strategies and evolving research.
Key Research Papers
Research papers are crucial for staying informed about the latest advancements in the field. They present peer-reviewed findings that can provide insights into treatment effectiveness, patient outcomes, and emerging therapeutic approaches.
A few noteworthy articles contribute significantly to the body of knowledge in this area:
- Mastocytoma in Adults: This paper delves into the clinical characteristics and management strategies specifically tailored for adults, providing a comparison with pediatric cases.
- Long-Term Outcomes of Adult Mastocytoma Patients: This longitudinal study tracks patient survival rates and quality of life, offering invaluable data for healthcare providers.
- Understanding Mast Cell Disorders: Covering basic biology, this research offers a foundation for understanding how mastocytoma relates to other mast cell disorders, creating a broader context for clinicians and researchers.
Reading these studies not only enhances one’s understanding of mastocytoma but also fosters a more nuanced perspective on how individual patient circumstances can widely vary.
Books and Resources for Understanding Mastocytoma
Books and comprehensive resources complement research papers by providing a detailed narrative, often enriched with case studies and clinical insights. They serve as helpful guides for both lay readers and medical professionals.
Consider the following resources:
- "Mastocytosis: Handbook of Clinical Strategies" - This book extensively covers the clinical aspects and management techniques for mastocytosis, a broader category that includes mastocytoma. It gives practical advice that can be directly applied to patient care.
- "Understanding Mast Cell Activation" - Aimed at both researchers and medical practitioners, this resource discusses mast cell biology and how these cells contribute to various disorders.
- Online Forums and Communities: Platforms such as Reddit can be invaluable for connecting with individuals facing similar conditions. Sharing experiences and tips can give insights not found in medical literature alone.
Incorporating these resources into one’s study not only fortifies the foundation of knowledge but also keeps healthcare professionals equipped for real-world applications and patient interactions.
"Knowledge is power, but it’s the application of that knowledge that leads to effective patient care."
To summarize, the integration of key research papers and insightful books serves to enhance a reader’s understanding of mastocytoma in adults. These resources not only fill the knowledge gaps but also present a platform for continued learning and adaptation in the ever-evolving landscape of medical research. By engaging with these materials, students, researchers, educators, and professionals can collectively contribute to improving outcomes and advancing the management of this complex condition.







