Understanding Constant Kidney Infections: A Comprehensive Analysis

Intro
Constant kidney infections represent a significant medical issue that affects many individuals. These recurrent infections can lead to substantial morbidity and impact the quality of life for those affected. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, symptoms, risk factors, and approaches to management is crucial. With a rise in global health awareness, this topic becomes more relevant than ever. It invites a comprehensive exploration into the nuances of kidney health and recurrent infections, shedding light on the challenges faced by patients and healthcare providers alike.
Background and Context
Overview of the Research Topic
Kidney infections, medically termed pyelonephritis, occur when bacteria ascend from the lower urinary tract to the kidneys. Constant or recurrent infections are defined by multiple episodes occurring within a specific timeframe. These infections commonly arise from organisms such as Escherichia coli, which are prevalent in urinary tract infections. Despite individual episodes being treatable, understanding why these infections persist is critical.
Historical Significance
Research surrounding kidney infections dates back several decades. Initially, studies focused on acute instances; however, more recent investigations highlight the importance of chronic conditions. Historical insight shows a trend toward identifying anatomical and physiological anomalies as underlying causes. The 20th century witnessed advances in imaging and diagnostic techniques, enhancing our understanding of associated factors, such as urinary tract obstructions and renal abnormalities. This evolution is pivotal in realizing that constant kidney infections require more than just symptomatic treatment—they necessitate a multidisciplinary approach.
Key Findings and Discussion
Major Results of the Study
Recent studies emphasize that recurrent kidney infections can lead to kidney damage or chronic kidney disease. The relationship between urinary stasis and recurrent infections points towards the necessity for prompt diagnosis and intervention. Research has also indicated a growing concern regarding antibiotic resistance, complicating management strategies. Understanding these factors is vital for developing effective treatment plans.
Detailed Analysis of Findings
- Prevalence: Numerous studies suggest that women are more likely to experience recurrent infections due to anatomical predisposition.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include fever, flank pain, and dysuria. Recognizing these early can mitigate further complications.
- Management Strategies: Long-term antibiotic prophylaxis can be beneficial for certain patients. However, it is essential to evaluate the risks of resistance and side effects.
- Impact on Quality of Life: Frequent infections disrupt daily activities and can lead to mental health issues among patients.
"Recurrent kidney infections highlight the need for personalized treatment plans that consider the individual’s medical history and lifestyle."
This comprehensive understanding of constant kidney infections sets the stage for further research and clinical discussions. It paves the way for improved patient outcomes through targeted strategies that address both the complexity of the infections and their broader health implications.
Prelims to Kidney Infections
Kidney infections, known medically as pyelonephritis, present significant health concerns that can affect various aspects of life. They are often caused by bacteria that ascend from the lower urinary tract. The importance of kidney infections lies in their potential to lead to serious health issues if left untreated or mismanaged. This article aims to provide an understanding of kidney infections, focusing on the complexities of their causes, symptoms, and treatments. By doing so, we hope to equip readers with knowledge that can facilitate better health decisions.
Definition and Overview
A kidney infection occurs when pathogens invade the kidneys, leading to inflammation and dysfunction. The condition can arise from lower urinary tract infections that ascend, often resulting in more severe symptoms and urgent treatment needs. The kidneys, vital organs responsible for filtering waste from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining electrolyte balance, can be significantly affected by infections.
Understanding the definition and overview of kidney infections is crucial for recognizing their potential impact on individual health. Early detection and treatment are paramount. Ignoring symptoms can lead to complications such as renal scarring, chronic kidney disease, and in severe cases, sepsis. Therefore, acknowledging the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for effective management.
Epidemiology of Kidney Infections
Kidney infections are more prevalent than some might think, affecting millions of individuals globally each year. They are particularly common in women due to anatomical differences that make ascending infections easier. According to research, approximately 1 in 5 women will experience a urinary tract infection in their lifetimes, with a significant portion progressing to kidney infections.
The age of onset can vary, but it often occurs in younger and middle-aged adults. Pregnant women, individuals with urinary tract abnormalities, and those with a history of diabetes are at an increased risk. Furthermore, geographical factors can influence the epidemiology of kidney infections, with higher incidence rates reported in certain regions due to variations in access to healthcare, hygiene practices, and public health initiatives.
"Understanding the epidemiology of kidney infections not only highlights the numbers but also points to the populations most at risk."
Recognizing the prevalence and distribution of kidney infections forms the basis for developing targeted prevention and treatment strategies. It also emphasizes the need for public awareness and education regarding this significant health issue.
Anatomy of the Urinary System
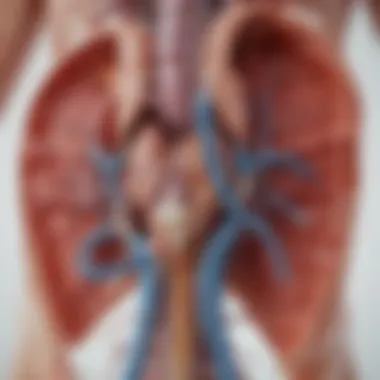
Understanding the anatomy of the urinary system is essential for grasping the complexities of constant kidney infections. The urinary system is not merely a collection of organs; it plays a pivotal role in filtering blood, producing urine, and regulating essential bodily functions. An in-depth comprehension of its structure and functionalities aids in identifying where infections might initiate and the systemic effects they can have.
Structure of the Kidneys
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located at the back of the abdominal cavity. They are about the size of a fist and are integral to the urinary system. Each kidney contains approximately one million functional units called nephrons. Nephrons are crucial for filtering waste from the blood and reabsorbing necessary substances. The outer layer of the kidney is called the renal cortex, which houses the nephrons. Inside this layer is the renal medulla, which is composed of triangular structures called renal pyramids that transport urine. At the center of each kidney lies the renal pelvis, a funnel-shaped area that collects urine before it moves to the ureters.
The structural design of the kidneys facilitates their filtration and excretion functions, making them highly efficient. Conditions such as kidney stones or abnormalities in structure can significantly increase the risk of infections, thus understanding kidney anatomy is vital in addressing these concerns.
Functions of the Kidneys
The kidneys perform several critical functions. They filter blood to remove waste, regulate fluid balance, and maintain electrolyte levels. The kidneys also play a role in blood pressure regulation through the renin-angiotensin system and contribute to blood cell production by releasing erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
Apart from these roles, kidneys help in maintaining the body's acid-base balance. This function is essential for overall health, as a stable pH level is critical for numerous metabolic processes. Any disruption in the kidney's functioning, whether due to infections or other underlying conditions, can lead to serious health issues.
Understanding the structure and functions of the kidneys is fundamental for recognizing the impact of persistent infections and for developing effective treatment strategies.
In summary, the anatomy of the urinary system, specifically the kidneys, provides vital insights into how infections can develop and their potential consequences. Recognizing these details enables both healthcare professionals and patients to take informed steps towards prevention and management.
Causes of Constant Kidney Infections
Understanding the causes of constant kidney infections is vital in addressing this serious health issue. Recognizing these causes can lead to better prevention strategies and more effective treatment options. The knowledge of underlying contributors is critical for patients, healthcare providers, and researchers alike. It provides insights into how to manage infections and ultimately improves patient outcomes. This section explores three main components: bacterial pathogens, anatomical abnormalities, and underlying health conditions.
Bacterial Pathogens
Bacterial pathogens are the primary culprits behind kidney infections. Escherichia coli is the most common bacteria responsible, accounting for a significant majority of cases. Other organisms like Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterobacter can also cause infections. The bacteria typically ascend from the lower urinary tract into the kidneys. Factors like urinary retention or incomplete bladder emptying can contribute to this ascension. Understanding how these pathogens operate offers insights into preventative measures, like maintaining proper hydration to ensure regular urination, which can help flush potential bacteria from the urinary tract.

- Preventive Strategies:
- Stay hydrated to promote healthy urine flow.
- Practice safe sexual habits to reduce bacterial introduction.
- Regularly empty the bladder to avoid stasis and bacterial growth.
Awareness of bacterial origins helps to formulate effective antibiotic therapies. Targeted treatments can be tailored based on the specific bacteria involved, improving recovery chances and reducing recurrence, therefore, having extensive knowledge about bacterial involvement is essential for proper management of kidney infections.
Anatomical Abnormalities
Anatomical abnormalities in the urinary system significantly increase the risk of recurrent kidney infections. Structural issues can interfere with normal urine flow or provide an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Some common abnormalities include urinary tract obstructions, congenital malformations, and kidney stones.
- Examples of Anatomical Issues:
- Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Presence of renal stones
Such conditions may lead to stasis of urine, allowing bacteria to thrive. They can also make it difficult for the body to completely clear any existing infections. Therefore, understanding these anatomical factors is critical. If these abnormalities are present, surgical interventions may be necessary. These procedures help restore normal urinary function and minimize the risk of kidney infections in the future.
Underlying Health Conditions
Underlying health conditions play a significant role in predisposing individuals to constant kidney infections. Diabetics, for instance, may experience duller immune response, making it harder for the body to combat infections. Additionally, conditions like chronic kidney disease or autoimmune disorders can complicate the infection dynamics.
- Key Conditions Increasing Risk:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Disorders affecting the immune system
These conditions may affect kidney function directly or indirectly, exacerbating the risk of kidney infections. Understanding this link encourages proactive management of chronic diseases, which can significantly lower the incidence of kidney infections. Regular check-ups and adherence to treatment plans are essential for mitigating these risks.
Effective management of underlying health conditions can lead to improved kidney health and reduced recurrence of infections.
In summary, identifying the causes of constant kidney infections is crucial. It not only helps in diagnosing and treating existing infections but also provides a framework for preventive strategies. Armed with this knowledge, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to combat the development of further infections.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Kidney Infections
Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic methods for kidney infections is vital for timely intervention and effective treatment. Recognizing the signs early can prevent complications and improve outcomes. In this section, we will look into the most common symptoms associated with kidney infections and the various methods employed for diagnosis.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of kidney infections can vary from person to person, but some signs are more prevalent than others. Typical symptoms include:
- Pain in the back, side, or abdomen: Patients often describe discomfort that can radiate from the back to the groin.
- Frequent urination: This symptom may present alongside a sense of urgency to urinate.
- Painful urination: Dysuria, or pain during urination, often signals an infection.
- Fever and chills: These systemic responses indicate a body's fight against the infection.
- Nausea and vomiting: These can occur due to the body’s stress from the infection.
These symptoms are crucial for individuals to recognize as they may prompt an earlier consultation with healthcare providers. Ignoring them could lead to worsening conditions or progression to more severe renal complications.
Diagnostic Methods
Effective diagnosis of kidney infections employs a variety of methods aimed at accurately assessing the presence of infection. Here are some key diagnostic approaches:
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is often the first step in diagnosing a kidney infection. This test examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine. One key characteristic of urinalysis is its ability to detect the presence of white blood cells, bacteria, and red blood cells. These elements often indicate an ongoing infection.
The benefit of this method lies in its effectiveness and minimal invasiveness. Urinalysis can be carried out quickly, allowing for rapid screening that aids in timely treatment decisions. However, a limitation is that it cannot confirm specific bacterial pathogens, which can necessitate further testing.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans play an important role in diagnosing kidney infections. These methods visualize the kidneys and surrounding structures, helping to identify any anatomical abnormalities, abscesses, or obstructions. One key aspect of imaging techniques is that they guide healthcare professionals in understanding the extent of the infection and any complications that may exist.
Using imaging can be beneficial in cases where infections are recurrent or complicated. However, the use of radiation in CT scans is a consideration, especially for certain patient populations, such as pregnant women.
Culture Tests
Culture tests, particularly urine cultures, are definitive in establishing the specific bacteria responsible for a kidney infection. By culturing urine, healthcare providers can identify the exact pathogen and determine its antibiotic sensitivity.
The uniqueness of culture tests lies in their ability to inform targeted treatment plans, enhancing the chances of successful recovery. This is especially important in cases where patients have recurrent infections or are resistant to standard antibiotics. However, culture tests can take longer to yield results compared to urinalysis.
Early and accurate diagnosis of kidney infections is essential for effective treatment and improved patient outcomes.
These diagnostic methods complement one another, offering a comprehensive approach to understanding kidney infections. Recognizing symptoms early, alongside effective diagnostic techniques, significantly impacts patient care and management.
Impact of Recurring Infections
Kidney infections, particularly when they are constant, have significant repercussions that extend beyond the immediate physical symptoms. Understanding the impact of recurring infections is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. These infections not only compromise renal function but also have far-reaching effects on daily life and mental well-being.
Physical Health Consequences

The direct physical implications of constant kidney infections can be severe. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining electrolyte balance. Recurring infections can lead to chronic kidney disease, which may gradually impair kidney function. In some cases, patients may experience elevated blood pressure or the development of uremia, a toxic condition resulting from kidney failure.
Moreover, persistent infections can cause scarring or damage to the kidney tissue. This physiological damage may result in painful symptoms and lead to complications such as sepsis, which is a life-threatening response to infection. Additionally, the overuse of antibiotics to treat recurrent infections can contribute to antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat.
Patients may also face limitations in their physical activities due to symptoms like fever, fatigue, or flank pain.
"Chronic kidney infections can create a cycle of illness that depresses overall health and well-being."
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional and psychological toll of enduring constant kidney infections is often underestimated. For many patients, recurring infections create a state of chronic stress and anxiety. The unpredictability of symptoms and the frequent need for medical interventions can lead to feelings of helplessness. Patients might feel like they are trapped in a cycle of illness, which may affect their motivation and self-esteem.
Depression is common among those dealing with constant health issues. Research shows that there is a direct link between physical health and emotional well-being, especially in chronic illness cases. This interplay suggests that effective management of kidney infections may require not just medical treatment, but also psychosocial support.
Patients might find themselves constantly worrying about the possibility of another infection, leading to a reluctance to engage in social activities or maintain relationships. Consequently, they may experience isolation, impacting their overall quality of life.
Treatment Approaches for Constant Kidney Infections
Effective treatment of constant kidney infections is essential for managing symptoms, reducing recurrence, and preserving kidney function. Understandably, patients and healthcare professionals are dedicated to identifying optimal strategies tailored to the individual’s specific circumstances. This section will discuss the primary treatment methods available for constant kidney infections, offering insights into their mechanisms, benefits, and considerations.
Antibiotic Therapies
Antibiotic therapies are the first line of defense against bacterial kidney infections. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include ciprofloxacin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The choice of antibiotic largely depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection and its sensitivity profile.
The primary benefit of antibiotic therapy is its targeted action against infection, often resulting in symptom relief within a few days. However, there are some considerations to keep in mind. Overuse of antibiotics can lead to resistance, making future infections more difficult to treat. Moreover, some individuals may experience side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions. Regular follow-up and sensitivity testing can help mitigate these risks.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where structural abnormalities or obstruction contributes to recurrent kidney infections, surgical interventions may be necessary. Procedures like ureteral stenting or pyeloplasty can correct anatomical issues, promoting better urinary flow and reducing infection risk. These surgical options are usually considered after conservative treatments have failed.
The advantage of surgical interventions lies in their potential to provide long-term solutions. Patients often experience fewer urinary tract infections post-surgery. However, surgery comes with inherent risks such as infection, bleeding, and recovery time. Patients should discuss with their healthcare provider the appropriateness of surgery based on individual health and specific conditions.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Some people explore alternative and complementary treatments to manage constant kidney infections, often alongside standard medical therapies. Herbal remedies such as cranberry extract and probiotics have garnered attention for their potential benefits. Cranberry is believed to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract wall, while probiotics may help enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms.
While these methods can offer support, their efficacy varies widely among individuals. There is limited clinical evidence confirming the effectiveness of these treatments, and they should not replace conventional therapies without proper medical guidance. Moreover, patients must ensure that any supplements do not interact with prescribed medications.
In summary, treatment approaches for constant kidney infections encompass a range of strategies, from antibiotic therapies to surgical interventions and alternative remedies. Each method presents its own benefits, risks, and considerations. A cooperative approach involving healthcare professionals is crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses the patient’s specific situation and enhances their overall kidney health.
Preventing Kidney Infections
Preventing kidney infections is a critical component in maintaining overall urinary health. Kidney infections, caused primarily by bacteria, can lead to serious health issues if they persist. Understanding how to effectively prevent these infections is vital for individuals at risk and those who have experienced recurrent issues. This section discusses the significant elements of prevention, including lifestyle adjustments and hygiene practices, which can greatly reduce the likelihood of infection.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making thoughtful lifestyle modifications can be instrumental in preventing kidney infections. Some important changes include:
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water helps to flush out harmful bacteria from the urinary tract. Sufficient hydration also supports kidney function and overall health.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can boost the immune system. Foods like cranberries have been noted for their potential in preventing urinary tract infections.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining an active lifestyle can improve circulation and immune responses, reducing infection risk.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is beneficial. Smoking can impair immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Weight Management: Obesity often correlates with a higher risk of kidney infections. Aiming for a healthy weight can help mitigate this risk.
By integrating these lifestyle changes, individuals can create a proactive approach towards preventing infections.
Hygiene Practices
Effective hygiene practices are equally essential in reducing the risk of kidney infections. Simple daily habits can make a significant difference, such as:
- Proper Wiping Techniques: Always wiping from front to back after using the restroom helps prevent bacteria from the anal region from entering the urethra.
- Frequent Handwashing: Regular handwashing, particularly before using the restroom and after handling food, can minimize the transfer of harmful bacteria.
- Wear Breathable Underwear: Cotton underwear allows for better airflow, preventing excessive moisture that can foster bacterial growth.
- Regular Urination: Avoiding prolonged periods without urination can help rid the body of bacteria. It is advisable to urinate after sexual activity to eliminate potential pathogens.
In summary, both lifestyle modifications and good hygiene practices are crucial in the prevention of kidney infections. They provide individuals with practical tools to safeguard their health, preventing painful and complicated future issues.
"Preventing kidney infections primarily involves a combined effort of healthy living and personal hygiene. Every small action counts in promoting better kidney health.”
By prioritizing these practices, individuals not only enhance their kidney health but contribute to overall well-being.
Long-term Management of Kidney Health
Long-term management of kidney health is a critical aspect when dealing with constant kidney infections. Maintaining kidney function and preventing the recurrence of infections ensures a better quality of life for patients. This management involves continuous strategies that include regular monitoring and strict adherence to treatment plans.
Regular evaluation of kidney function is essential. Frequent check-ups help to detect any early signs of deterioration in kidney health. Management also needs to consider patient-specific factors such as age, other health conditions, and lifestyle choices that can affect kidney health.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring plays a key role in the long-term management of kidney health. It involves a systematic approach to check kidney function at defined intervals. This is important because kidney infections can lead to complications if not managed properly.
Monitoring may include:

- Blood tests: These are done to check levels of creatinine and electrolytes, helping to assess kidney function.
- Urinalysis: This test can reveal signs of infection or damage in the kidneys.
- Imaging studies: Techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans can help visualize any structural abnormalities in the urinary tract that might contribute to recurring infections.
By understanding and tracking these indicators, healthcare professionals can make timely interventions, adjusting treatment as necessary. Challenges may arise, such as patient non-compliance to scheduled appointments, which the healthcare team should address through education and encouragement.
Adherence to Treatment Plans
Adherence to treatment plans is another cornerstone of long-term kidney management. Patients with constant kidney infections must follow prescribed medications, lifestyle modifications, and follow-up recommendations diligently. Non-adherence can lead to a cycle of recurrent infections and increased healthcare costs.
Key components of a treatment plan often include:
- Antibiotic regimens: These should be taken exactly as prescribed to eliminate infection effectively.
- Lifestyle modifications: Changes in diet and hydration are often necessary to support kidney health and reduce infection risks.
- Regular follow-ups: Scheduled visits with healthcare providers help ensure that treatment is effective and that any needed adjustments are made promptly.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in supporting patient adherence. They can use various strategies, such as educational sessions or reminders, to emphasize the importance of following the plan.
The long-term health of the kidneys significantly impacts overall wellbeing, making adherence to treatment non-negotiable.
By focusing on these aspects of long-term management, patients can improve their health outcomes and minimize complications associated with constant kidney infections.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
The role of healthcare professionals is vital in managing constant kidney infections. Their expertise not only informs treatment protocols but also affects patient outcomes significantly. Healthcare professionals come from various fields, including nephrology, urology, nursing, and infectious diseases. This mixed approach ensures that the treatment plan is comprehensive, considering all aspects of a patient's health.
Interdisciplinary Care Teams
Interdisciplinary care teams play an essential role in the management of kidney infections. These teams consist of specialists who collaborate to provide holistic care. For instance, a nephrologist may focus on the kidney's function while an infectious disease specialist treats the underlying infections. This cooperation helps identify underlying causes, such as anatomical abnormalities or chronic diseases, which are crucial for effective treatment.
Moreover, these teams facilitate communication between different healthcare providers and the patient. Clear communication helps ensure that all aspects of patient care are aligned. This alignment can include medication management, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-ups.
Having an interdisciplinary care team increases the likelihood of better outcomes, as they can adjust treatment approaches based on a patient's evolving needs.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Patient education and empowerment are also critical components of effective kidney infection management. When patients understand their condition, they are more likely to adhere to their treatment plans. This knowledge includes understanding urinary tract health, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical help.
Empowerment can take many forms. It may involve educating patients about medications they are prescribed or advising them about lifestyle modifications, such as proper hydration and improved hygiene practices. Additionally, patients can benefit from learning about the importance of regular check-ups and monitoring to avoid future infections.
Healthcare professionals must engage in ongoing education efforts to ensure that patients are well-informed. As stated in a recent study, "Patient knowledge significantly influences health outcomes, especially in chronic conditions like kidney infections." This underscores the necessity of fostering a collaborative environment where healthcare providers and patients work together toward better health.
Recent Research and Advances
Research into constant kidney infections has expanded significantly in recent years. Understanding these infections requires continuous examination of both clinical practices and innovative treatments. This section explores recent findings that influence how healthcare professionals view and manage kidney infections.
Innovations in Treatment
Innovations in treatment for kidney infections include the development of new antibiotic formulations and alternative therapies. Healthcare researchers work to combat antibiotic resistance, a significant concern. New antibiotics, such as fosfomycin and meropenem, show promise in treating resistant strains of bacteria. These antibiotics are useful during cases of complicated urinary tract infections.
Moreover, research into immunotherapy is gaining traction. Immunotherapy aims to enhance the body's immune response against infections. This approach may lower the recurrence rate and promote long-term kidney health.
Additionally, dietary supplements, like cranberry extract and probiotics, are under investigation. While traditional treatments serve immediate purpose, these alternatives could support traditional medicines to reduce infection frequency.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Ongoing clinical trials play a vital role in understanding and enhancing treatment for kidney infections. Numerous trials are examining novel medications, including more effective antibiotic regimens and adjunct therapies. These efforts aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce recurrence rates, and lower treatment-related side effects.
Clinical trials focus on various aspects, including:
- Efficacy of new antibiotics: Investigating how new formulations can combat resistant strains.
- Immunotherapies: Evaluating the effectiveness of enhancing the immune response in preventing infections.
- Combination therapies: Studying the effect of using complementary treatments alongside traditional antibiotics.
The findings from these trials not only enhance current understanding but also guide future clinical practices. Monitoring and reporting outcomes from these studies ensures that both patients and healthcare providers can benefit from ongoing advancements.
"Recent developments in research are essential to shaping the future of kidney health management and infection treatment."
Continued investment in research and clinical trials is critical in tackling the growing challenge of constant kidney infections. Innovations and discoveries contribute to a deeper understanding of the complexities behind these infections and lead to more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
End
The conclusion serves as a crucial element in this article by synthesizing the comprehensive information surrounding constant kidney infections. It brings together the various aspects discussed throughout the text, underscoring the significance of understanding these infections for both health professionals and patients. The importance of this topic cannot be overstated. It encapsulates not only a summary of the medical facts but also highlights the broader implications for patient quality of life, treatment efficiency, and ongoing health monitoring practices.
Summary of Key Points
In this article, several key points have emerged regarding constant kidney infections. These include:
- Definition and understanding of kidney infections and their prevalence.
- Anatomy of the urinary system, emphasizing the role and structure of the kidneys.
- Causes of recurring infections such as bacterial pathogens, anatomical issues, and underlying health conditions.
- The symptoms displayed by individuals suffering from these infections and methods for proper diagnosis.
- Various treatment approaches, emphasizing antibiotics, potential surgical interventions, and alternatives that may benefit chronic patients.
- Critical prevention strategies through lifestyle and hygiene.
- The role of healthcare professionals in providing a cohesive and knowledgeable approach.
- Recent research developments and innovations regarding treatment effectiveness and ongoing clinical trials.
Each point contributes to a robust understanding of this persistent health challenge and serves as a foundation for informed action by individuals and healthcare providers.
Final Thoughts on Kidney Health
The issue of constant kidney infections demands attention not only for its medical implications but also for its impact on patient lives. Maintaining kidney health is integral, and a multifaceted approach is vital. This involves awareness of the factors leading to infections, understanding symptoms, and seeking timely medical advice when necessary. All patients should prioritize regular monitoring and adherence to prescribed treatment plans. Through education and proactive strategies, the community can mitigate the effects of these infections.
"Knowledge is power, especially in healthcare. Understanding the intricacies of kidney infections empowers patients to take charge of their health."
By grasping the content presented in this article, readers are better equipped to navigate the complexities of kidney infections, promoting healthier lives and better overall outcomes.







