Cirrhosis of the Liver: Rash Pictures and Significance


Intro
Liver cirrhosis presents a major health challenge worldwide. It can develop from various underlying causes and significantly affects multiple organ systems. Among the less discussed manifestations of this condition are the skin rashes that frequently accompany liver damage. These rashes can vary in appearance and severity. Understanding these symptoms is vital for diagnosis and treatment of the underlying liver condition.
The aim of this article is to provide a thorough examination of the connection between liver cirrhosis and skin rashes, as well as the implications this relationship carries for patient care and management.
Understanding Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is a condition that indicates advanced liver damage and scarring. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This section provides foundational knowledge about cirrhosis, highlighting its significance in relation to skin manifestations, especially rashes. By comprehending cirrhosis, readers can better recognize signs that may indicate liver dysfunction and its implications on overall health.
Definition and Overview
Cirrhosis occurs when the liver becomes severely scarred due to various factors, resulting in compromised liver function. The liver is essential for metabolic processes, detoxification, and the production of critical proteins. Once cirrhosis develops, it is usually irreversible and can lead to severe complications, including liver failure and liver cancer.
Understanding its definition and overview is key to grasp how liver damage can extend beyond internal symptoms to manifest on the skin. Often, this organ’s distress reveals itself through rashes or other dermatological signs.
Etiology of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis can arise from multiple factors. Understanding these factors helps in both prevention and treatment. Key causes include:
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease encompasses a spectrum of liver disorders, including alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. It is characterized by excessive intake of alcohol, leading to inflammation and liver cell damage. This etiology is significant as it emphasizes the need for awareness regarding alcohol consumption.
A hallmark of alcoholic liver disease is the development of fatty liver, a stage that can progress to more severe forms if drinking continues. Recognizing the risks associated with alcohol can encourage individuals to consider moderation or abstinence, making this a vital aspect in the exploration of cirrhosis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is recognized as a leading cause of cirrhosis globally. It is linked to metabolic conditions like obesity and diabetes. The primary feature of NAFLD is the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often without inflammation.
This condition is increasingly relevant due to rising obesity rates. As awareness grows regarding lifestyle-related diseases, understanding NAFLD is beneficial in addressing lifestyle modifications that could prevent progression to cirrhosis.
Hepatitis infections
Hepatitis B and C are viral infections known to contribute significantly to cirrhosis. They lead to chronic liver inflammation, where persistent infection ultimately results in scarring. People often contract these infections through blood exposure or unsafe practices.
Highlighting the role of hepatitis emphasizes the importance of vaccination and safe practices. It also allows readers to understand the preventive measures that can avert the risk of ending up with cirrhosis.
Genetic factors
Certain genetic disorders, such as hemochromatosis or Wilson disease, can predispose individuals to cirrhosis. These inherited conditions lead to abnormal metal accumulation in the liver, causing damage over time.
Understanding genetic factors is essential, as it underscores the role of family health history in assessing individual risk. Genetic predisposition raises awareness and might prompt individuals to undergo screenings or lifestyle changes to mitigate risks.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
The symptoms of cirrhosis can be vague early on but become more pronounced as the disease progresses. Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and jaundice. Notably, dermatological manifestations like rashes and pigmentation changes also begin to surface.
Identifying these symptoms early is critical. Recognizing that skin changes can signal underlying liver issues might prompt quicker medical consultation, ultimately leading to better management of the disease and improving outcomes for those affected.
Skin Manifestations Associated with Cirrhosis
Skin manifestations in cirrhosis are more than just cosmetic concerns; they act as important indicators of underlying liver pathology. This article examines how these skin changes can alert healthcare providers and patients to potential liver dysfunction. Recognizing these rashes can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective management of liver disease.
Overview of Cutaneous Changes
Cirrhosis can lead to numerous cutaneous changes, each providing insight into liver health. These changes often result from alterations in liver function, including impaired metabolism and hormonal imbalances. The skin can exhibit signs like discoloration, lesions, or abnormal vascular formations.
Such manifestations may not be present in early stages of cirrhosis, but as the disease progresses, they become more apparent. Prompt recognition of these changes can be critical in managing cirrhosis and improving patient outcomes.

Types of Rashes Linked to Cirrhosis
Spider angiomas
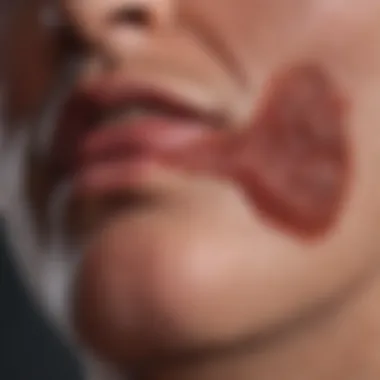
Spider angiomas are small, spider-like blood vessels that appear on the skin surface. A key characteristic of spider angiomas is their red color and the presence of a central arteriole with smaller radiating vessels. This rash is significant because it suggests increased estrogen levels, often found in liver cirrhosis, particularly in men.
The presence of spider angiomas is useful for identifying patients who might have developed hepatic dysfunction. One advantage of recognizing this rash is its visibility and easy identification, making it a common topic in discussions of liver disease.
Palmar erythema
Palmar erythema manifests as redness on the palms and fingers. The key characteristic of this condition is the lack of blistering or scaling, which differentiates it from other dermatological issues. Palmar erythema is a useful clinical sign in establishing the presence of liver cirrhosis.
The unique feature of this rash is that it may vary in intensity across patients. Some may have only faint redness, while others may display pronounced symptoms. Its presence confirms the need for thorough liver function evaluation and categorization of chronic liver diseases.
Jaundice
Jaundice is characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, resulting from elevated bilirubin levels. This condition serves as a direct indicator of liver dysfunction. Its key characteristic, the yellow discoloration, makes jaundice a highly visible sign of underlying liver issues.
Recognizing jaundice is beneficial as it leads patients to seek medical care promptly. Its visibility helps in awareness among patients and relatives regarding liver health, prompting further investigation into potential causes.
Xanthomas
Xanthomas appear as yellowish, fatty deposits on the skin, indicative of lipid metabolism disorders. These rashes can be associated with cholestasis, a common condition in cirrhosis. Their unique feature is that they often resemble small bumps or plaques on the skin.
The identification of xanthomas is significant as they can signal the need for a cholesterol profile evaluation. While xanthomas may concern some patients due to their appearance, recognizing them can provide an opportunity for lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments.
Visual Identification of Rash Patterns
Recognizing the different rash patterns associated with cirrhosis is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Each pattern conveys essential information about the individual's liver health and guides further clinical assessment. To enhance understanding, healthcare providers often utilize visual aids in education and diagnosis. This way, the interplay between the skin and liver is clarified, offering a deeper perspective on patients' conditions.
Diagnostic Approaches
Understanding the diagnostic approaches for cirrhosis of the liver, especially regarding its skin manifestations, is essential for accurate detection and management. This section emphasizes how different methods can aid in unveiling the underlying issues associated with liver diseases. Employing a combination of dermatological assessments, laboratory tests, and imaging studies can provide a comprehensive profile of the patient's health. Moreover, identifying the early signs of liver cirrhosis through skin changes can significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Role of Dermatological Assessment
Dermatological assessment plays a critical role in the diagnostic landscape of cirrhosis. Physicians use this specialized evaluation to observe skin changes that may indicate liver dysfunction. Various cutaneous symptoms, such as spider angiomas or palmar erythema, can serve as external markers of internal liver conditions.
These assessments provide immediate clues regarding liver health. They help clinicians determine the severity of liver disease based on visible symptoms. Additionally, dermatologists can distinguish between skin conditions that are benign and those linked to systemic issues, guiding further investigation if required.
Laboratory Tests for Liver Function
Laboratory tests for liver function are crucial in confirming the diagnosis of cirrhosis. These tests help assess the liver’s ability to perform its functions and also detect any abnormalities. Here are some key aspects:
Liver function tests
Liver function tests measure various enzymes and proteins in the blood. They are beneficial because they provide insights about liver health in a non-invasive way. A key characteristic of these tests is their ability to detect elevated enzyme levels, indicating liver damage. Common tests include ALT, AST, alk phos, and bilirubin.

These tests can identify problems before significant liver damage occurs, giving patients a chance for timely intervention. However, they can also vary due to factors like alcohol intake or medication use, requiring careful interpretation.
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) offers valuable information about a patient's overall health and can be indicative of cirrhosis. It measures levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The key characteristic of CBC is its ability to reveal anemia or thrombocytopenia, conditions often associated with chronic liver disease. This makes CBC a popular choice for initial assessments.
The unique feature of a CBC is its simplicity and rapid results, which can be critical in emergency situations. However, a CBC does not directly assess liver function, necessitating comprehensive follow-up testing for a full picture of hepatic health.
Imaging studies
Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, are essential tools for the evaluation of liver cirrhosis and its complications. They provide visual insights into the liver's size, structure, and any potential lesions. A key characteristic is their non-invasive nature, allowing detailed views without surgical intervention.
Imaging studies are especially beneficial in visualizing portal hypertension and assessing liver morphology. However, their limitations include the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel, which can restrict access in some cases.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a critical step in the evaluation of liver cirrhosis and its cutaneous manifestations. This process involves distinguishing cirrhosis from other liver diseases or conditions with similar skin symptoms. For example, rashes could also result from autoimmune diseases, viral hepatitis, or drug reactions.
Correctly identifying the underlying cause is vital for determining the appropriate management strategies. Thus, a thorough history, physical examination, and appropriate use of diagnostic tools must occur. By clarifying the diagnosis, healthcare professionals can enhance treatment plans aimed at both liver health and skin presentations.
Management and Treatment of Cirrhosis
The management and treatment of cirrhosis are pivotal in improving patient outcomes and overall health. Cirrhosis indicates significant liver damage, which can result in various complications, including hepatic encephalopathy and liver cancer. Proper management strategies can help mitigate these risks, prolong survival, and enhance the quality of life. It is essential to identify the etiology of cirrhosis for better-targeted treatments and lifestyle alterations. This article will explore several strategies and aspects of treatment that are critical for individuals coping with the disease.
General Treatment Strategies
Effective management of cirrhosis typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, pharmacological interventions, and regular monitoring. The following elements are key:
- Dietary modifications: Nutrition plays a crucial role. Patients often need to limit salt intake to manage fluid retention. A balanced diet, emphasizing protein and vitamin intake, supports liver function.
- Regular physical activity: Exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall well-being. It is vital to tie this into a physician's advice to avoid overexertion.
- Avoiding alcohol and certain medications: Ethanol exacerbates liver damage. Non-prescription drugs, especially certain pain relievers, may also pose risks.
- Regular screenings: Continuous assessments help detect complications early. Blood tests and imaging studies support ongoing evaluations of liver function and disease progression.
Specific Management of Skin Manifestations
Skin manifestations are common among cirrhosis patients and need specific management approaches:
Topical therapies
Topical therapies focus on addressing skin symptoms localized on the surface. They can provide immediate relief from discomfort, as rashes and lesions can cause itching or pain. Common agents include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and emollients to hydrate the skin. These treatments are often deemed beneficial due to their localized effects and minimal side effects. However, one must be aware that prolonged use might lead to skin thinning or discoloration.
Systemic treatments
Systemic treatments refer to medications that affect the body as a whole, targeting the underlying liver condition. This could include corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents. These drugs can significantly reduce systemic inflammation and are particularly useful for more extensive skin lesions associated with diseases like autoimmune liver disorders. While systemic treatments can provide effective relief, they are also tied to risks such as immune suppression, making close monitoring vital.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures aim to manage risks associated with cirrhosis progression and skin issues. Common recommendations include regular dermatological check-ups and sun protection strategies to mitigate photosensitivity that often accompanies liver diseases. Preventing potential complications is crucial, especially in advanced liver conditions. However, focusing solely on preventive measures without addressing existing symptoms could lead to discomfort or worsening of the condition.
Importance of Multidisciplinary Care


Multidisciplinary care is essential in managing cirrhosis effectively. A team that includes gastroenterologists, dermatologists, nutritionists, and even mental health professionals can offer coordinated care. This approach ensures that all aspects of a patient's health are addressed, improving overall management effectiveness. Regular communication between specialists can lead to well-rounded treatment plans, optimizing medication usage, and integrating lifestyle adjustments, creating a comprehensive support system for the patient.
Prognosis and Future Considerations
Understanding the prognosis of cirrhosis is vital for patients, healthcare providers, and caregivers. Cirrhosis can significantly impact quality of life, and its progression can vary greatly. Knowledge of potential outcomes aids in managing expectations and planning treatment. Prognosis refers to the likely course of the disease and chances of recovery. It involves assessing factors like the cause of liver damage, stage of liver disease, and overall patient health.
Long-term Management of Cirrhosis
Long-term management of cirrhosis focuses on slowing disease progression and preventing complications. Regular monitoring is essential. Patients should undergo routine liver function tests and imaging studies to assess liver health. Management strategies include:
- Lifestyle changes: Avoiding alcohol is critical. A balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight can improve outcomes.
- Medication adherence: Patients must follow prescribed treatment plans to manage symptoms and other health conditions.
- Regular check-ups: Frequent visits to healthcare providers can detect changes in liver function early.
Individuals with cirrhosis may also develop portals hypertensions and liver cancer. Therefore, they need to be educated about symptoms that necessitate immediate attention, such as unusual bleeding or jaundice. This understanding can significantly affect their quality of life.
Research Advances in Cirrhosis Treatment
Research in cirrhosis treatment is progressing rapidly. The focus is on finding novel therapies that can reverse liver damage or offer better disease management. For example, newer antifibrotic agents are being tested in clinical trials. These agents aim to reduce fibrosis, potentially halting progression to liver failure.
In addition, studies on gene therapy are emerging. This approach looks to modify genetic factors contributing to liver disease. Combining traditional treatment with advanced therapies may provide new options for patients. It is essential to stay informed about these developments, as they could dramatically impact future treatment landscapes.
Implications for Clinical Practice
Understanding the prognosis and future considerations of cirrhosis is critical for clinical practice. Knowledge of potential outcomes enables healthcare professionals to provide tailored care.
Clinicians must consider:
- Patient education: Informing patients about their condition fosters better management.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: Physicians, nutritionists, and mental health professionals should work together to provide comprehensive care.
- Ongoing education: Keeping abreast of research developments aids in patient treatment strategies.
Overall, understanding cirrhosis’s prognosis strengthens the healthcare system's response to liver disease. It underscores the importance of early detection and effective management.
Finale
The conclusion serves as a critical component of this article, summarizing the significance of understanding the relationship between cirrhosis of the liver and its associated cutaneous manifestations. Recognizing the link between skin rashes and liver dysfunction can provide valuable insights, not only for healthcare professionals but also patients and their families. The integration of dermatological symptoms in the assessment of cirrhosis enhances the approach to diagnosis and treatment, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Moreover, emphasizing the importance of timely identification of symptoms ensures that individuals with liver disease receive appropriate care and management. In this context, the role of education and awareness cannot be overstated. By communicating the features and implications of various skin manifestations, individuals can gain the knowledge necessary to advocate for their health and navigate the complexities of cirrhosis treatment.
Recap of Key Points
- Understanding Cirrhosis: The article provided a detailed examination of cirrhosis, its causes, symptoms, and prognosis. It highlighted how the liver's functioning is integral to overall health and how its impairment can lead to a spectrum of clinical indications.
- Skin Manifestations: Various types of rashes associated with cirrhosis were discussed, including spider angiomas, palmar erythema, jaundice, and xanthomas. These signs play a crucial role in clinical assessment and can prompt further investigation into liver health.
- Diagnostic Approaches: The importance of dermatological assessments and laboratory tests were outlined as essential tools in confirming liver dysfunction. Distinguishing between different types of rashes is critical for accurate diagnosis.
- Treatment Strategies: Various management approaches, including topical and systemic therapies for skin manifestations, were reviewed. The article also highlighted the need for a multidisciplinary approach in handling cirrhosis, with collaboration across various specialties.
- Raising Awareness: The connection between skin symptoms and liver disease underscores the necessity for increased awareness among patients and practitioners alike. Recognizing early signs can lead to timely intervention and better health outcomes.
Call for Increased Awareness
The call for increased awareness is an essential plea in the context of liver disease and its manifestations. Education on the relation between liver cirrhosis and skin rashes can empower individuals to recognize signs early and seek medical attention promptly.
Healthcare providers should prioritize this aspect in their education materials and patient consultations. Increased awareness can help demystify the symptoms and promote proactive behaviors toward health management.
In community and healthcare settings, campaigns could focus on disseminating information. This can include workshops, informational brochures, and online resources to ensure a broader reach.
Patients and families equipped with knowledge will contribute to a more informed public, leading to better recognition of health issues associated with liver cirrhosis.
"Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world." – Nelson Mandela
Individuals are encouraged to stay informed and vigilant about their health. The acknowledgment of skin changes as potential indicators of serious liver issues can enhance monitoring and support the need for interventions at appropriate stages.







